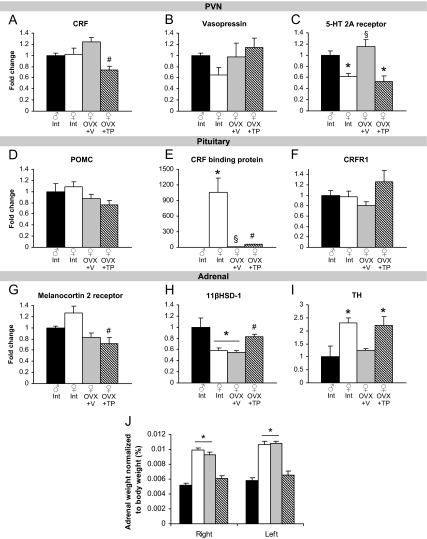
Figure 3.
Effects of sex and gonadal hormones on stress-related gene expression in primary tissues of the HPA axis. A, TP exposure in females reduced CRF mRNA in the PVN. #, P < 0.05, different from OVX+V. B, There were no differences in expression of vasopressin in the PVN. C, Intact and TP-treated females displayed lower 5-HT 2A receptor than males in the PVN. *, P < 0.05, compared with males. Expression was increased in OVX+V females. §, P < 0.05, different from intact and TP-treated females. D and F, There were no differences in POMC or CRF receptor-1 in the pituitary. E, There is a dramatic sex difference in CRF binding protein. *, P < 0.05, compared with males. OVX+V females also displayed greater expression than males but reduced from intact females. §, P < 0.05, different from all other groups. TP exposure in females increased CRF binding protein mRNA. #, P < 0.05, different from all other groups. G, TP treatment in females reduced melanocortin 2 receptor mRNA in the adrenal gland. #, P < 0.05, different from intact females. H, 11βHSD-1 mRNA was reduced in intact and OVX+V females (*, P < 0.05, different from males) and was increased by TP treatment. #, P < 0.05, different from OVX+V females. I, Intact and OVX+TP females displayed greater expression of TH than males. *, P < 0.05, different from males. J, Sex differences in adrenal weight were masculinized by TP treatment. Both the right and left adrenal glands were heavier in intact and OVX+V females compared with males and OVX+TP females. *, P < 0.05.