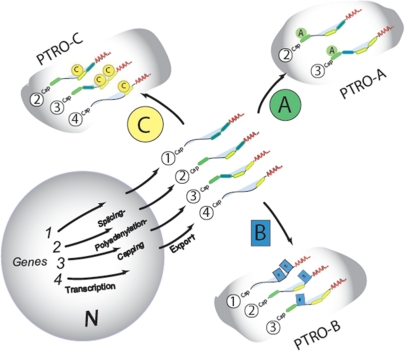
Figure 3.
Multiple copies allow multiple combinations of mRNAs. Illustration of the multiple lives of each mRNA based on the posttranscriptional RNA operon/regulon model (16). Functionally related mRNAs are “clustered” in time and space such that the proteins encoded by them can be coordinately produced in concert. Each of the four mRNAs has the potential to be a member of more than one subset because the protein it encodes serves multiple functional roles in different cellular processes. The colored circles represent different RBPs or different posttranslationally modified isoforms of a given RBP that bind to the colored bars in the 3′ or 5′ UTRs. Noncoding RNAs that bind in combination with RBPs to sequences in these mRNAs can affect posttranscriptional outcomes such as RNA stability and translation. Posttranscriptional RNA Operons (PTRos) are coordinated subsets of functionally related mRNAs in association with regulatory RBPs and noncoding RNAs that are spliced, transported, stabilized, localized, or translated in a coherent manner. Multiple PTRos can share certain mRNAs to form overlapping posttranscriptional regulons that coordinate the production of several related subsets of functionally related proteins.