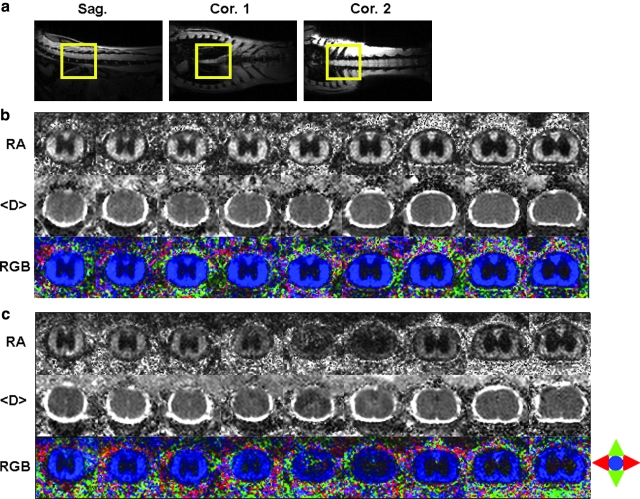
FIG. 4.
(a) Scout sagittal and coronal images, (b) serial transverse in vivo diffusion tensor images of the control, and (c) injured cords are demonstrated. Nine contiguous transverse (or axial) images were acquired encompassing T7-T10 vertebrae level (voxel size = 39 μm x 39 μm (zero-filled); slice thickness = 1 mm). Relative anisotropy (RA) and apparent mean diffusivity (<D>) are displayed in scale of 0–1.414 and 0–2 μm2/ms. The parenchyma of the spinal cord is hypointense compared to the surrounding bright CSF in the <D> map. The gray-white matter contrast is clearly seen in the RA map. The coherent directionality of white matter is obvious in the color-coded RA map where red is left to right, green is up and down, and blue is in and out of the image plane. The epicenter of the injury is easily identified from the RA map.