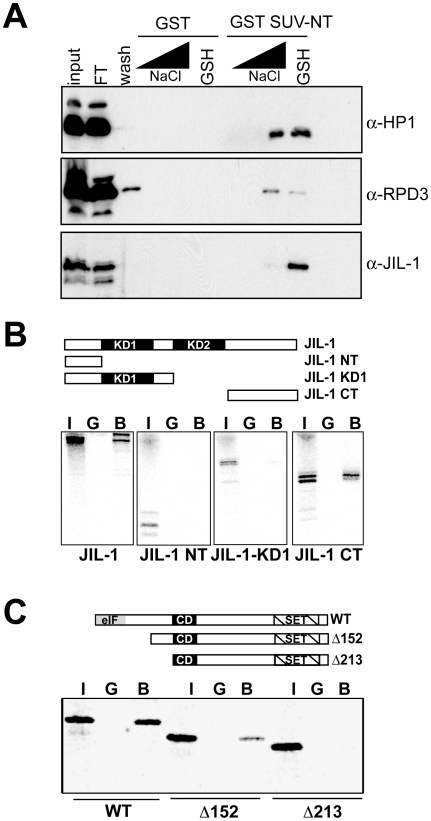
Figure 1. Identification of the chromosomal kinase JIL-1 as a novel interaction partner of SU(VAR)3–9.
(A) Western Blot analysis of the eluates (250, 500, 750 mM Nacl and reduced Glutathion, GSH) from the indicated columns, identifies JIL-1 as a novel interactor of SU(VAR)3–9. 15 µl of each fraction were separated by SDS-PAGE and subjected to Western Blot analysis using the indicated antibodies (FT = flow through). (B) The JIL-1 C-terminus mediates the interaction with SU(VAR)3–9. Top: Schematic representation of the JIL-1 derivatives used for the in vitro translation reaction indicating the characteristic domain structure of JIL-1 (KD1/KD2 = kinase domain 1 and 2). Bottom: GST pull-downs using bacterially expressed GST or GST SU(VAR)3–9NT together with the indicated JIL-1 constructs. (C) A region within the N-terminus of SU(VAR)3–9 interacts with JIL-1. Top: Schematic representation of the SU(VAR)3–9 constructs used for the in vitro translation reaction indicating the characteristic domain structure of the protein (eIF = homology region to the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2; CD = chromodomain; SET: SET domain). Bottom: GST pull-downs using bacterial expressed GST or GST JIL-1 full length together with the indicated recombinant SU(VAR)3–9 proteins. The GST fusion proteins were expressed in E. coli, purified, and incubated with in vitro translated, 35S-labeled JIL-1 or SU(VAR)3–9 (and deletions thereof). I = 5% input used for the precipitation; G = GST; B = Bound.