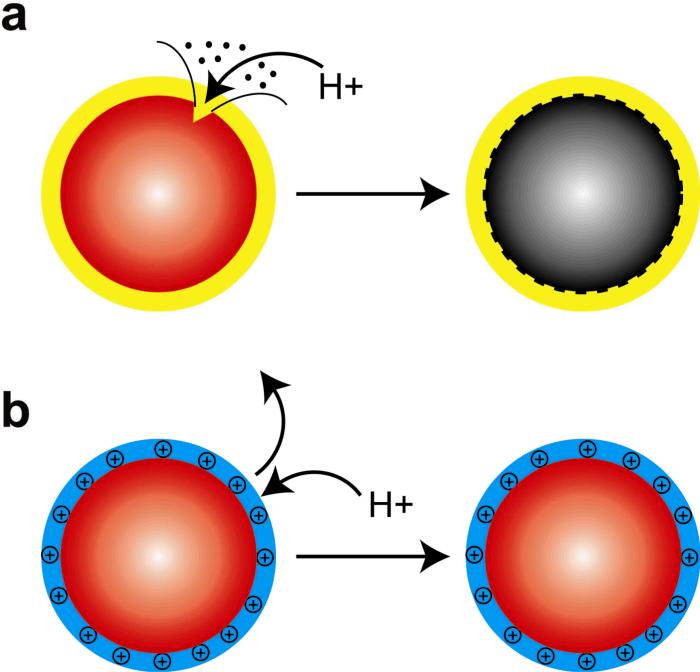
Figure 1. Schematic diagrams of (a) acid-etchable and (b) proton-resistant quantum dots.
Acid etching leads to surface defects and fluorescence quenching, as observed for QDs coated with amphiphilic polymers or lipids. The use of cationic “proton-resistant” surface coatings prevents free protons from reaching the nanocrystal surface, thus protecting QDs from acid-induced etching.