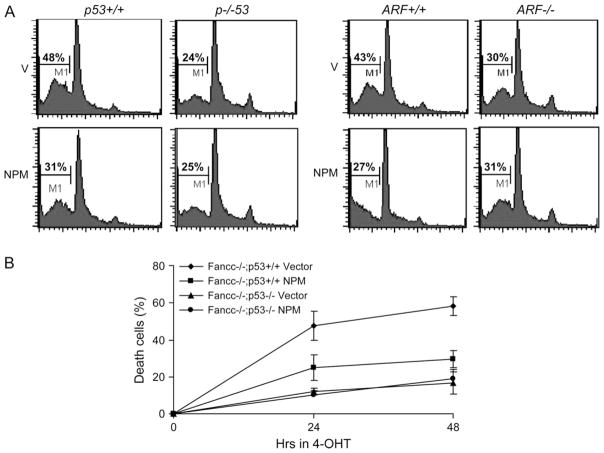
Fig. 3.
NPM inhibits Myc-induced apoptosis requires a functional p53–ARF pathway. (A) Effect of NPM over-expression on Myc-induced apoptosis in p53- and ARF-null cells. Genetically matched p53 or ARF WT and null MEFs were infected with pMSCVpuro empty vector (V) or pMSCVpuro-NPM retrovirus. After 72 h puromycin selection, the cells were infected with the MycER viruses. Forty-eight hours after transduction, cells were cultured in the presence of 125 nM 4-hydroxy tamoxifen (4-OHT) for 24 h and analyzed for subdiploid DNA content by flow cytometry. (B) p53-dependent cell death in Fancc−/− cells expressing activated c-Myc. p53+/+, Fancc−/− or p53−/− and Fancc−/− MEFs were infected with pMSCVpuro empty vector (V) or pMSCVpuro-NPM retrovirus. After 72 h puromycin selection, the cells were infected with the MycER viruses. Forty-eight hours after transduction, cells were cultured in the presence of 125 nM 4-hydroxy tamoxifen and cell viability was measured at 0, 24 and 48 h after transfer to 4-hydroxy tamoxifen-containing medium.