Fig. 1.
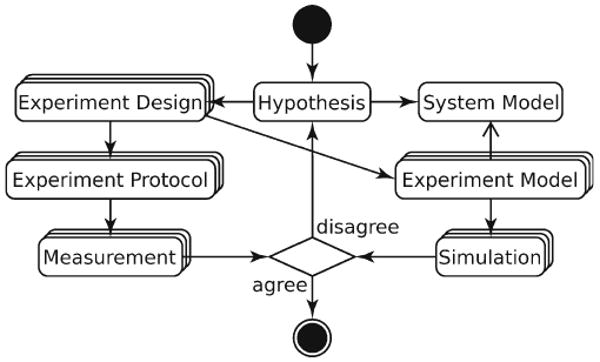
Application of scientific method to quantitative biology. Mechanistic Hypothesis about a biological system leads to a System Model, a quantitative description of system components and their interactions. To test the Hypothesis, the system is treated in a controlled manner and its behavior is measured. The ideas, assumptions, and, possibly, hypotheses involved in the treatment are parts of Experiment Design. The Measurement obtained by following the Experiment Protocol is compared with Simulation. To make the comparison meaningful, all Simulations need to have same physical meaning and dimensionality as their corresponding Measurements. Therefore, an Experiment Model, an in silico counterpart of Experiment Protocol, is derived from each Experiment Design. Experiment Models interacting with the System Model produce Simulations that are quantitatively compared with the Measurements.
