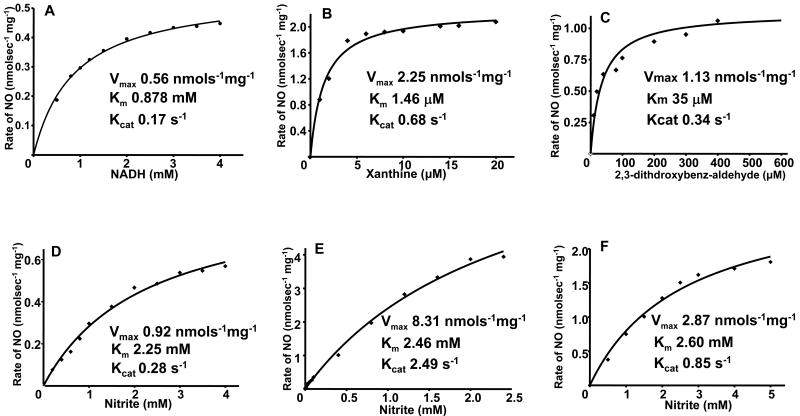
Fig. 3.
Kinetics of NO generation from XO as a function of reducing substrate or nitrite concentration. A shows the effect of [NADH] on the rate of NO generation from 0.04 mg/ml XO and 1.0 mM nitrite. B shows the effect of [xanthine] on the rate of NO generation from 0.02 mg/ml XO and 1.0 mM nitrite. C shows the effect of [2,3-dithdroxybenz-aldehyde] on the rate of NO generation from 0.02 mg/ml XO and 1.0 mM nitrite. D shows the rate of NO generation by 0.04 mg/ml XO and 1.0 mM NADH in the presence of 0.2-4 mM nitrite. E shows the rate of NO generation by 0.02 mg/ml XO, 5 μM xanthine in the presence of 5 μM-2.5 mM nitrite. F shows the rate of NO generation by 0.02 mg/ml XO, 40 μM 2,3-dithdroxybenz-aldehyde in the presence of 0.5 mM-5 mM nitrite. For each of these graphs, the corresponding fits (solid lines) Km, Vmax, and Kcat data were obtained using the Michaelis-Menten equation. Adopted from [35].