Abstract
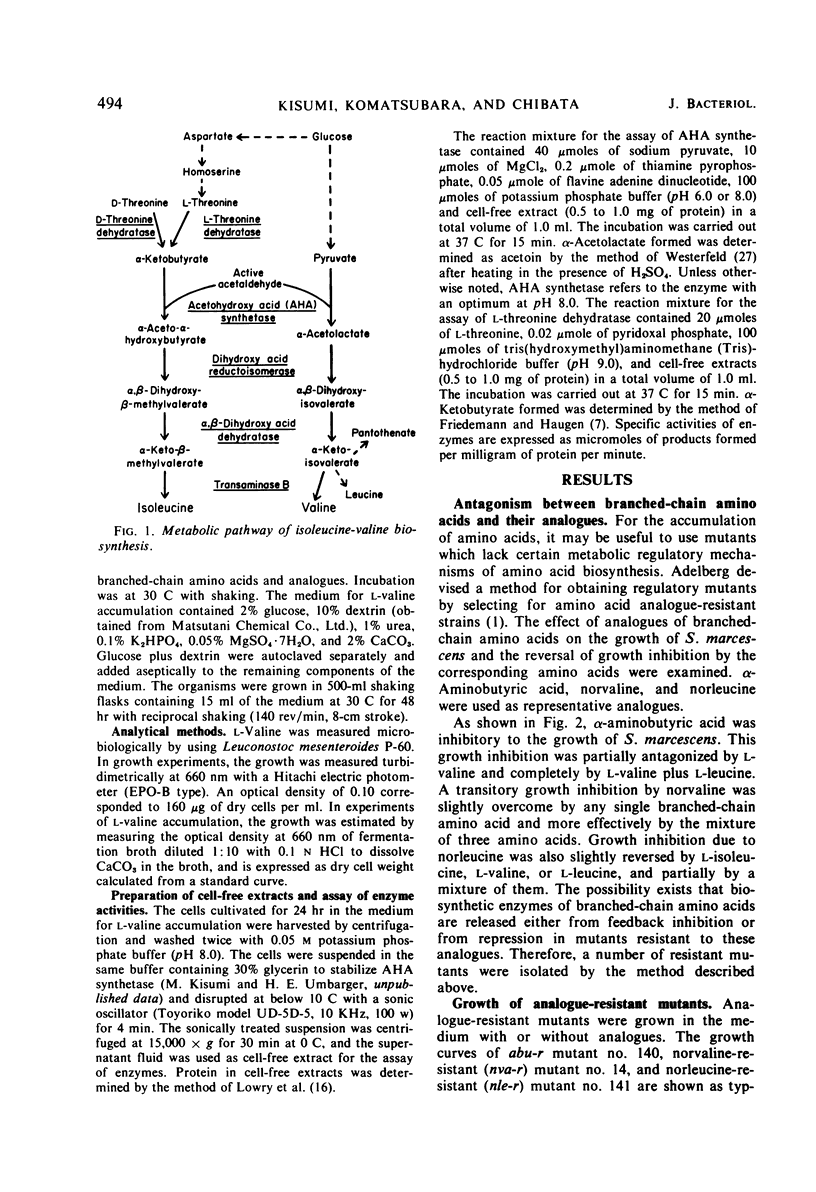
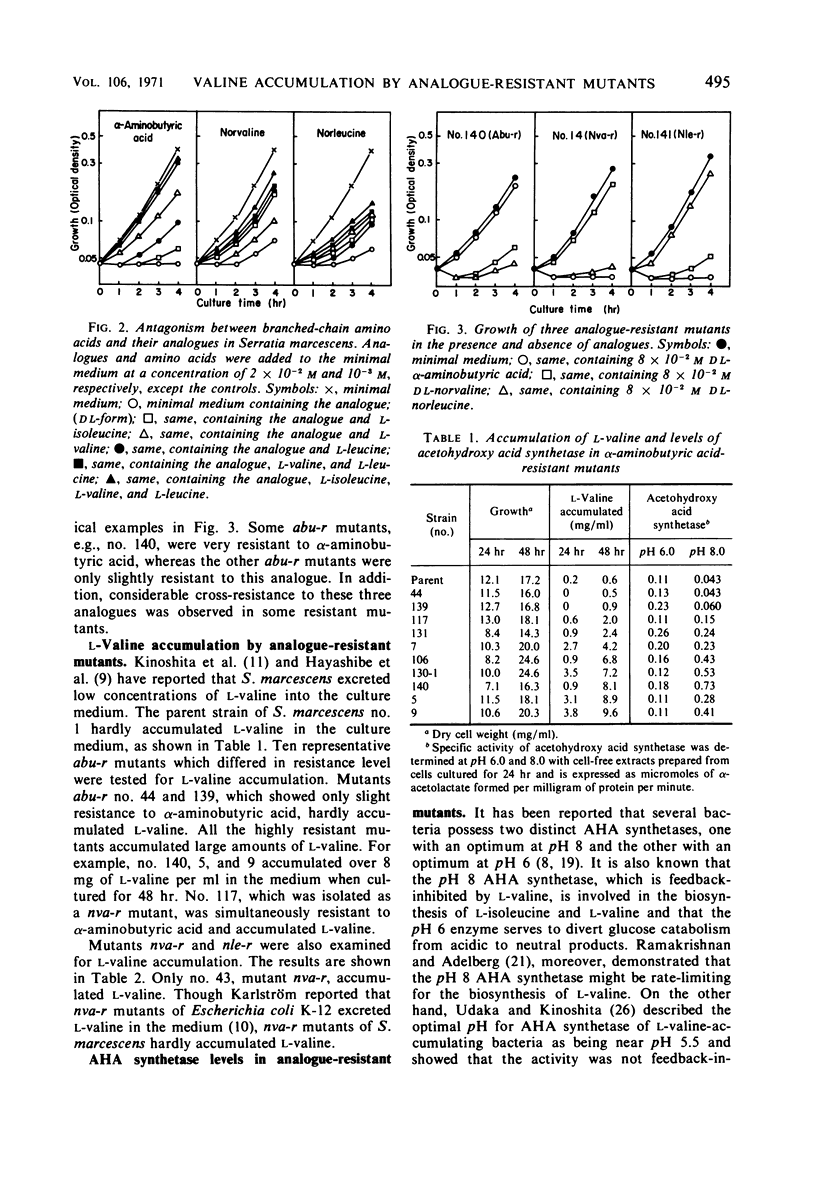
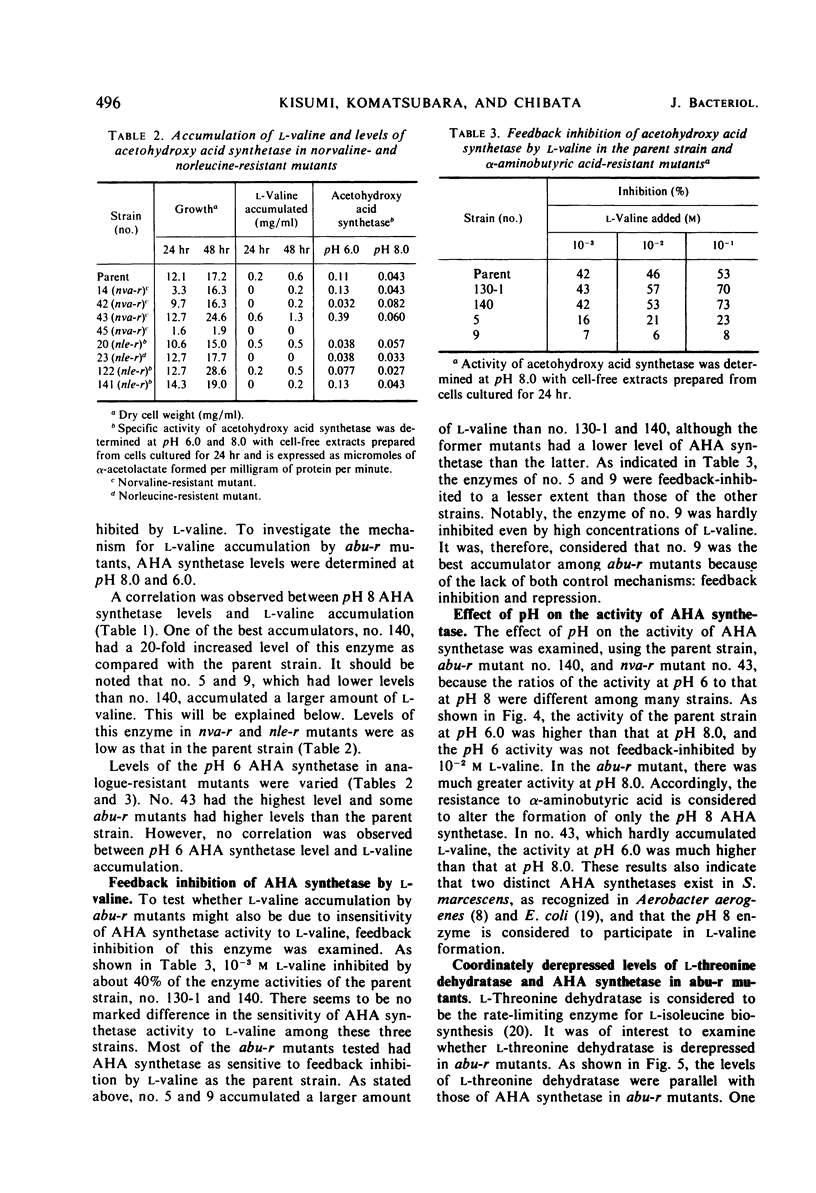
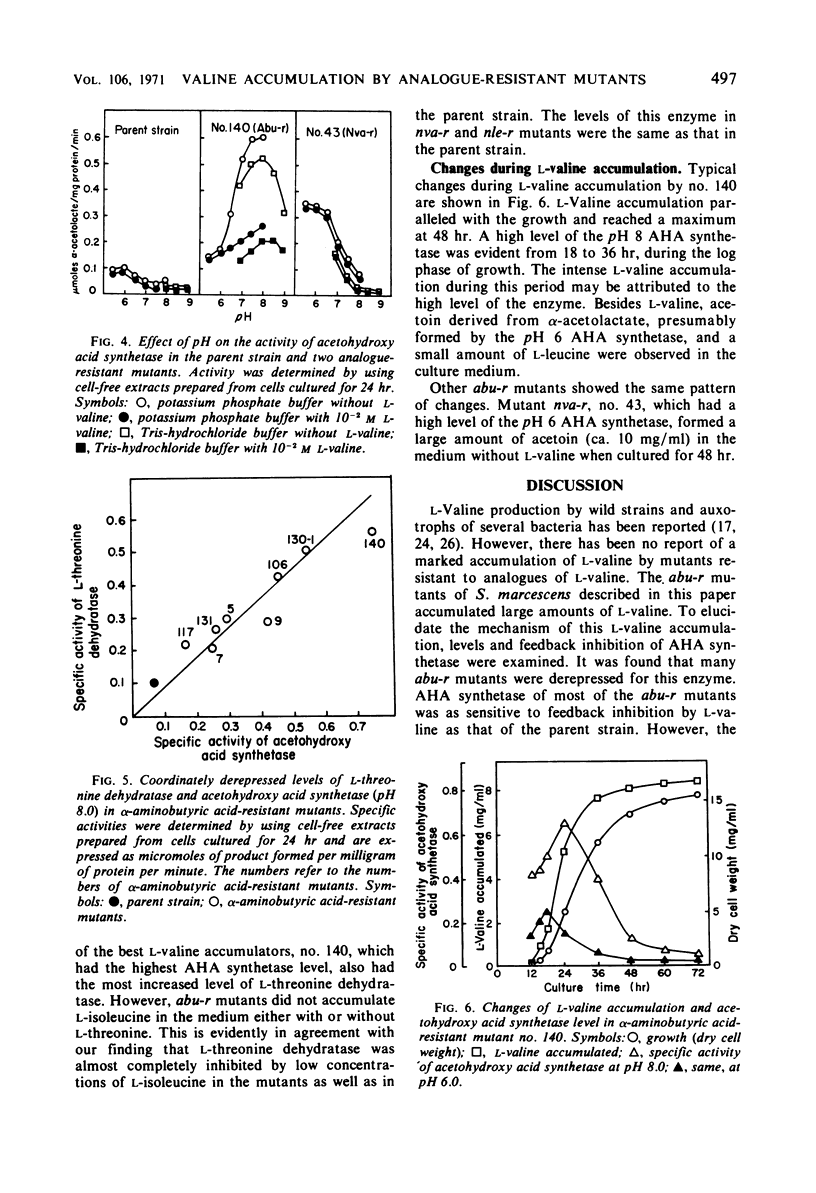
α-Aminobutyric acid, norvaline, and norleucine, which are analogues of branched-chain amino acids, inhibited the growth of Serratia marcescens. The inhibitory effect of these three analogues was counteracted by branched-chain amino acids. A number of mutants resistant to these analogues were isolated. α-Aminobutyric acid-resistant (abu-r) mutants markedly accumulated l-valine in the culture medium, but the other analogue-resistant mutants did not. Acetohydroxy acid synthetase, which seems to be rate-limiting for the biosynthesis of l-valine, was derepressed in abu-r mutants. One of the abu-r mutants, no. 140, which accumulated over 8 mg of l-valine per ml, had about a 20-fold increase in the enzyme level. Most of the abu-r mutants had acetohydroxy acid synthetase activity which was sensitive to feedback inhibition by l-valine to the same extent as in the parent strain. However, the enzyme of two of abu-r mutants was less sensitive to l-valine, and one of the two was the best valine accumulator.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADELBERG E. A. Selection of bacterial mutants which excrete antagonists of antimetabolites. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):326–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.326-326.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN G. N., ADELBERG E. A. Kinetics of incorporation of p-fluorophenylalanine by a mutant of Escherichia coli resistant to this analogue. J Bacteriol. 1958 Sep;76(3):328–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.76.3.328-330.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calvo J. M., Freundlich M., Umbarger H. E. Regulation of branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis in Salmonella typhimurium: isolation of regulatory mutants. J Bacteriol. 1969 Mar;97(3):1272–1282. doi: 10.1128/jb.97.3.1272-1282.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. D., MINGIOLI E. S. Mutants of Escherichia coli requiring methionine or vitamin B12. J Bacteriol. 1950 Jul;60(1):17–28. doi: 10.1128/jb.60.1.17-28.1950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowden L., Lewis D., Tristram H. Toxic amino acids: their action as antimetabolites. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:89–163. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freundlich M., Clarke L. P. Control of isoleucine, valine and leucine biosynthesis. V. Dual effect of alpha-aminobutyric acid on repression and endproduct inhibition in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968 Dec 23;170(2):271–281. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(68)90007-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALPERN Y. S., UMBARGER H. E. Evidence for two distinct enzyme systems forming acetolactate in Aerobacter aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1959 Dec;234:3067–3071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISUMI M., ASHIKAGA Y., KATO J., CHIBATA I. Studies on the isoleucine fermentation. II. On the mechanism of isoleucine formation and threonine dehydrase. J Biochem. 1962 Dec;52:400–408. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127636. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISUMI M., KATO J., CHIBATA I. STUDIES ON THE ISOLEUCINE FERMENTATION. 3. THE INCORPORATION OF D-THREONINE-2-C14 AND UNIFORMLY LABELED GLUCOSE-C14 INTO ISOLEUCINE. J Biochem. 1964 Nov;56:450–456. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a128016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISUMI M. Studies on the isoleucine fermentation. I. Screening of organisms and investigation of cultural conditions. J Biochem. 1962 Dec;52:390–399. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a127635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEAVITT R. I., UMBARGER H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism in Escherichia coli. XI. Valine inhibition of the growth of Escherichia coli strain K-12. J Bacteriol. 1962 Mar;83:624–630. doi: 10.1128/jb.83.3.624-630.1962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C. Roles of amino acid activating enzymes in cellular physiology. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):701–719. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.701-719.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RADHAKRISHANAN A. N., SNELL E. E. Biosynthesis of valine and isoleucine. 2. Formation of alpha-acetolactate and alpha-aceto-alpha-hydroxybutyrate in Neurospora crassa and Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1960 Aug;235:2316–2321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. I. GENETIC DEREPRESSION OF ENZYME FORMATION. J Bacteriol. 1964 Mar;87:566–573. doi: 10.1128/jb.87.3.566-573.1964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN T., ADELBERG E. A. REGULATORY MECHANISMS IN THE BIOSYNTHESIS OF ISOLEUCINE AND VALINE. II. IDENTIFICATION OF TWO OPERATOR GENES. J Bacteriol. 1965 Mar;89:654–660. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.3.654-660.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szentirmai A., Szentirmai M., Umbarger H. E. Isoleucine and valine metabolism of Escherichia coli. XV. Biochemical properties of mutants resistant to thiaisoleucine. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1672–1679. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1672-1679.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


