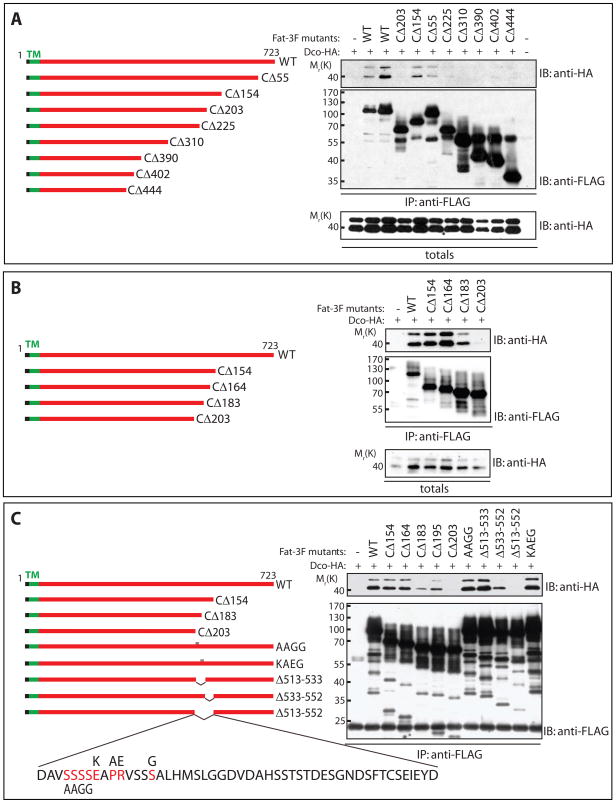
Figure 2. Dco interacts with the cytoplasmic domain of Fat.
Lysates from HEK293T cells expressing HA-tagged Dco together with 3FLAG-tagged variants of FatΔECD were subjected to immunoprecipitation with α-FLAG antibody and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
A) Dco was detected in immunoprecipitates of full-length FatΔECD, comprised of the transmembrane and entire intracellular portion of Fat, and in immunoprecipitates from versions of FatΔECD lacking 55 and 154 C-terminal amino acids (CΔ55 and CΔ154). Versions of FatΔECD lacking more than 203 amino acids (CΔ203) failed to pull down Dco.
B) While FatΔECD lacking 154 C-terminal amino acids (CΔ154) can strongly interact with Dco, deletion of 183 amino acids (CΔ183) weakens the Dco interaction, and deletion of 203 amino acids (CΔ203) completely abolishes the interaction.
C) Internal deletions of 39 amino acids (Δ513–552) from the cytoplasmic portion of FatΔECD eliminates interaction with Dco, while removal of 19 of these internal residues (Δ533–552) weakens but does not abolish the interaction. Mutation of conserved residues within this region (AAGG or KAEG) does not block Fat interaction with Dco.