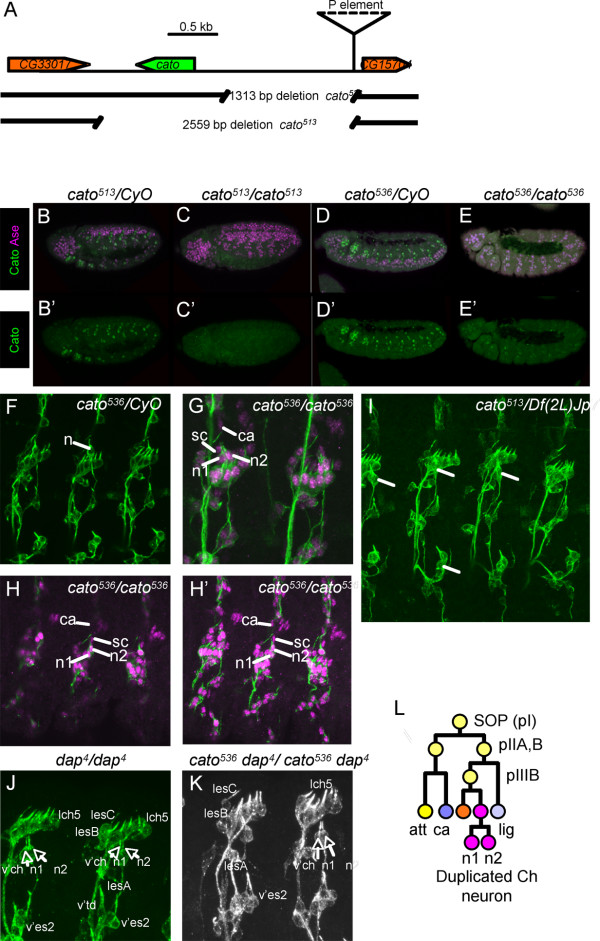
Figure 4.
Mutation of cato results in duplicated v'ch1 neurons. (A) Schematic of cato genomic region showing the location of the P-element and excision deletions. (B-E) Expression of Cato protein (green) is absent or strongly reduced in cato mutant embryos (Ase expression shown in magenta) (B, B') Heterozygous cato513/CyO embryo. (C, C') Homozygous cato513/cato513 embryo. (D, D') Heterozygous cato536/CyO embryo. (E, E') Homozygous cato536/cato536 embryo. (F-K) Late stage embryos stained with 22C10 (green) for sensory neurons and anti-Cpo (magenta) for nuclei of neurons and support cells. Cells of the v'ch1 chordotonal organ are indicated: n = duplicated v'ch1 neurons; sc = unduplicated scolopale cells; ca = unduplicated cap cells. (F) Heterozygous cato536/CyO embryo, showing wild-type 22C10 pattern. (G, H) Homozygous cato536/cato536 embryos, showing duplicated v'ch1 neurons (n1, n2). In (H) several confocal sections are shown. (I) Hemizygous cato513/Df(2L)Jp7 embryo, showing duplicated v'ch1 neurons. (J) Homozygous dap4/dap4 embryo stained with 22C10, showing duplicated v'ch1 neurons. Selected other neurons are labelled, and show no obvious duplication. (K) Double homozygous dap4cato536/dap4cato536 embryos stained with 22C10, showing similar phenotype to each single mutant in which v'ch neurons are duplicated but not adjacent neurons. (L) Schematic summary of the proposed neuronal duplication phenotype.