Figure 3. Retinyl Esters Synthesized by RPE and Retinal Membranes from All-trans-Retinol.
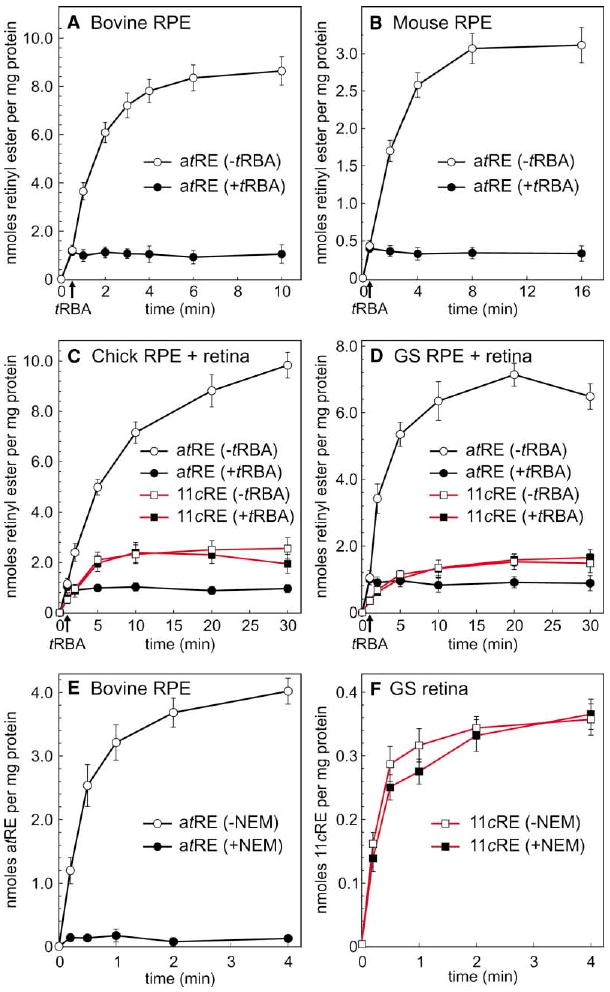
(A) Time course of all-trans-retinyl ester (atRE) synthesis by bovine RPE membranes in the absence (open circles) or presence (filled circles) of tRBA inhibitor. Arrow on the baseline indicates the time of tRBA addition. (B) Time course of all-trans-retinyl ester synthesis by mouse RPE membranes in the absence or presence of tRBA inhibitor. (C) Time course of all-trans-retinyl ester (circles, black lines) or 11-cis-retinyl ester (11cRE, squares, red lines) synthesis by chicken combined RPE + retinal membranes in the absence (open figures) or presence (filled figures) of tRBA inhibitor. (D) Time course of all-trans-retinyl ester or 11-cis-retinyl ester synthesis by ground-squirrel combined RPE + retinal membranes in the absence or presence of tRBA inhibitor. (E) Time course of all-trans-retinyl ester synthesis by bovine RPE membranes plus (open circles) or minus (filled circles) pre-treatment with NEM. (F) Time course of 11-cis-retinyl ester synthesis by ground-squirrel retinal membranes plus (open squares) or minus (filled squares) pre-treatment with NEM. For each experiment, the indicated all-trans- and 11-cis-retinyl esters were the only retinyl esters formed, shown as nmols per mg protein. Error bars show standard deviations (n = 4).
