Figure 2.
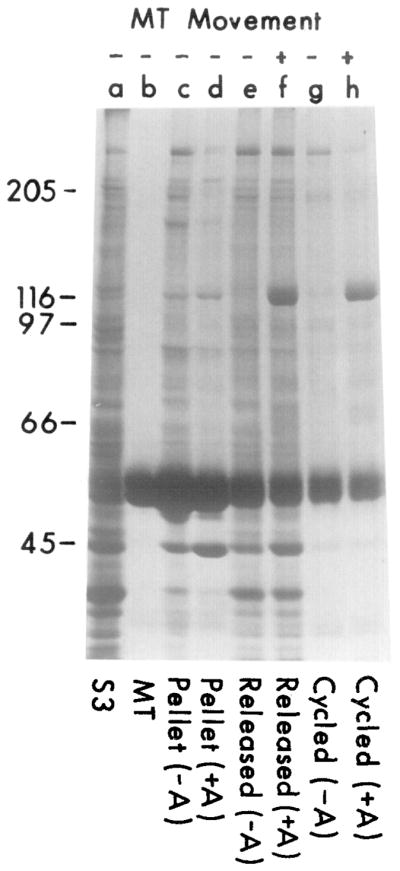
Cosedimentation of a Translocator from Squid Optic Lobes with Purified Microtubules in the Presence of AMP-PNP, and Its Subsequent Release by ATP
Soluble supernatant from squid optic lobes (S3, lane a) was incubated with 100 μg/ml of purified microtubules (lane b) in the presence or absence of 5 mM AMP-PNP as described in Experimental Procedures. Material released from microtubules by 5 mM ATP and 0.1 M KCl (45 min; 4°C) from AMP-PNP-treated samples (lane f) shows both a prominent band at 110 kd and movement-inducing activity; neither characteristic is associated with the supernatant of the untreated samples (lane e) or the final microtubule pellets resuspended in an equal volume of MTG with 2 mM ATP (lanes c and d) after ATP release.
The ATP-released translocator (lane f) was tested for rebinding to microtubules. The sample was diluted 5-fold in MTG (to reduce the concentration of ATP/KCl) and incubated with new microtubules (100 μg/ml) in the presence or absence of 5 mM AMP-PNP (15 min; 23°C). The microtubules were pelleted and washed, and proteins were released with 5 mM ATP and 0.1 M KCl for 45 min at 23°C. Material released from the AMP-PNP-treated sample contained the 110 kd polypeptide (lane h) and also induced movement (+); neither characteristic was prominent in the control (AMP-PNP-untreated) sample (lane g).
