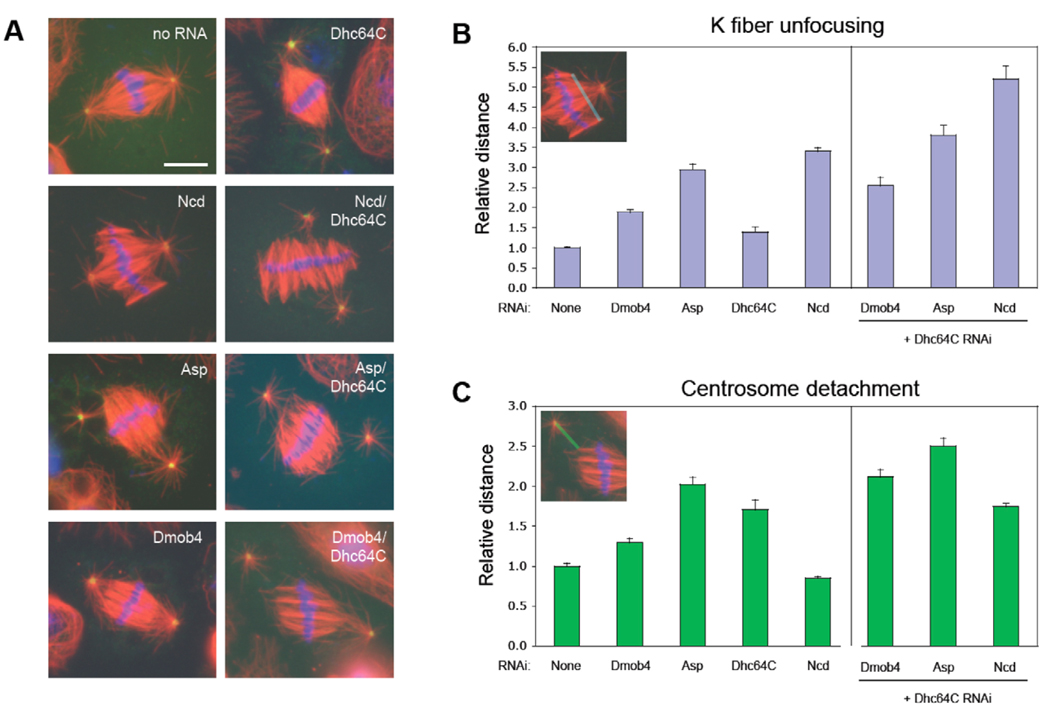
Fig. 3.
Double RNAi experiments suggest that the Drosophila Mob4 (Dmob4) phenotype is more similar to Asp than dynein or Ncd. (A) Representative mitotic spindle morphology after RNAi of the genes indicated. (α-tubulin, red; Dgrip84, green; DNA, blue; bar, 5 µm.) (B) Quantitation of K fiber unfocusing in metaphase spindles. The relative mean width of K fiber minus ends – the distance between the minus ends of the outermost K fibers at each pole (blue line in inset) relative to control cells [average 2.08±0.03 µm (mean±s.d.)] – is shown after RNAi of the gene(s) indicated. RNAi of Mob4, Asp or Ncd induced significant increases in the focal width of K fibers relative to that of control cells, whereas Dhc64C had a minimal effect. Co-depletion of Dhc64C and Ncd had a strong synergistic effect, whereas the synergism in cells co-depleted of Dhc64C and either Asp or Mob4 was minimal. [Error bars indicate the s.d. of the average K fiber unfocusing distance measured in three independent experiments (n>45 spindles for each trial).] (C) Quantitation of centrosome detachment in the same spindles measured in (B). The distance of the gap between the centrosome (Dgrip84-staining foci that nucleate astral microtubules) and the minus end of the K fiber lying closest to the centrosome (green line in inset), relative to control cells [average 1.92±0.07 µm (mean± s.d)] is shown. RNAi of Mob4, Asp or Dhc64C, but not Ncd, caused an increase in centrosome detachment (statistically significant difference for Mob4 RNAi and control cells; P<0.0001). Co-depletion of Dhc64C and either Asp or Mob4 produced a synergistic increase in centrosome detachment, whereas no synergism was observed for co-depletion of Dhc64C and Ncd.