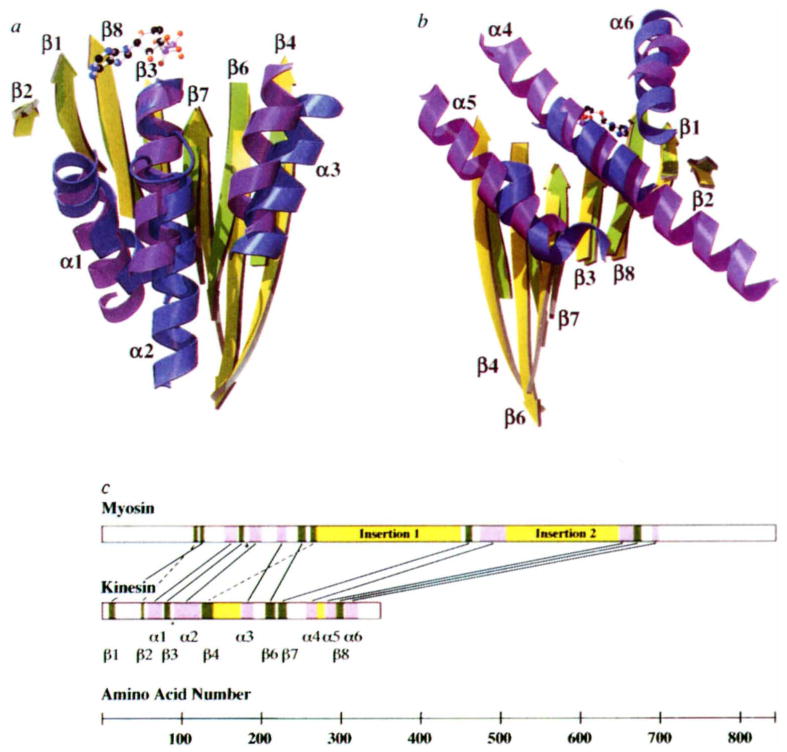
FIG. 2.
Comparison of overlapping secondary structure in kinesin and myosin. The overlap was achieved by aligning nine α-carbon atoms (kinesin amino acids 84–92 and myosin 178–186) in the P-loops of the two structures. The similarity between kinesins and myosins was first noted when the ncd tertiary structure18 was aligned with other proteins in the coordinate data bank12 (L. Holm, personal communication). a, Front view of the molecule, showing overlapping β-sheets and the three front α-helices. Secondary structure elements of kinesin are indicated. Myosin residue numbers refer to chicken skeletal muscle myosin. Shown are: β-strands (kinesin (k) yellow; myosin (m), green); left to right, β2, k50–k52, m116–119; β1, k9–k15, m122–m126; β8, k295–k302, m668–m675; β3, k79–k84, m173–m177; β7, k222–k231, m457–m463; β6, k206–k216, m247–m255; β4, k126–k138, m263–m268. Helices (kinesin, blue; myosin, purple); left to right, α1, k58–k74, m155–m169; α2, k91–k122, m186–m199; α3, k176–k189, m220–m231. b, Rear view of the molecule, showing overlapping β-sheets and the three rear α-helices. β-strands, same as in a, but rotated by 180°; α-helices, left to right, α5, k281–k292, m649–m665; α4, k257–k269, m475–m506; α6, k306–k320, m690–m697. c, Placement of corresponding structural elements in the linear sequence of kinesin and myosin. Helices and strands are indicated in purple and green, respectively. Insertions in the core motor domains are shown in yellow. In myosin, these insertions contain elements that interact with actin33. Lines connect overlapping structural elements; broken lines indicate structural elements that are in a different relative location in the primary sequence; the asterisk indicates the position of the P-loops.