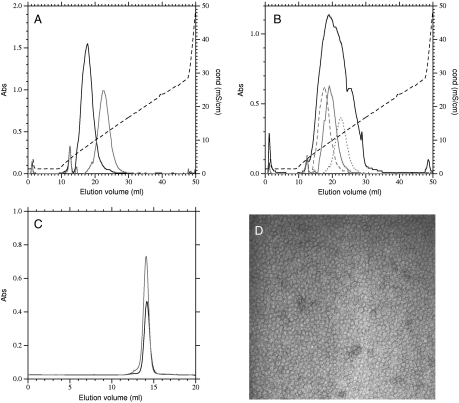
Fig. 2.
Purification and analysis of LH2 complexes. (A) Elution profile of B800–850 type (Black) and B800–820 type (Gray) LH2 complexes from a resource Q anion-exchange column. Complexes were loaded onto the column, washed with 20 mM Tris pH8.0 0.05% DM, and separated with a 200–500 mM NaCl gradient in the same buffer. (B) Elution profile of LH2 complexes from cells synthesizing a mixture of B800–820 and B800–850 type complexes (Black), using the same conditions as above. Three of the colored fractions were rechromatographed (Gray) after desalting and all fractions were eluted as a symmetric peak centered on the original fraction. (C) Size-exclusion chromatography of B800–820 type (Dark Gray), B800–850 type (Black) and mixed-type LH2 (Light Gray) complexes. Complexes isolated by anion-exchange chromatography were concentrated and loaded onto a Superose 6 (GE Healthcare) column eluted at 0.2 ml/ min with 20 mM Tris pH8.0 containing 0.05% DM. All complexes eluted at the same volume, corresponding to monomeric complexes. (D) Transmission electron micrograph of negatively stained LH2 complexes purified by anion-exchange chromatography.