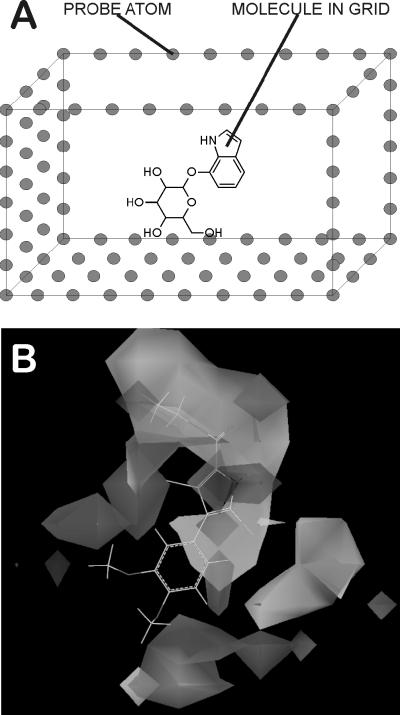
Figure 2. 3D QSAR.
3-Dimensional Quantitative Structure Activity Relationships (3D QSAR) are models generated by taking into account the 3-dimensional positions of various physicochemical characteristics of a set of overlapped molecules and the effect they have on drug potency [94,99]. A) Molecules are overlapped and placed in a superimposed grid with extents of several Angstroms in all directions. Each grid point is treated as a probe; neutral carbon atoms probe for Van der Waal's interactions, while charged atoms probe Coulombic interactions. Fragments can also be used as probes for elucidating H-bond donors or acceptors. Simple physics equations calculate the energy (data value) at each grid point. These data are examined for trends using PLS, MLR or AI algorithms fit to the biological properties of the molecules. B) The resultant map indicates regions where certain physicochemical parameters, e.g., charge or steric bulk, are tolerated (or not tolerated), which serves as an aid to chemists designing analogs with improved properties.