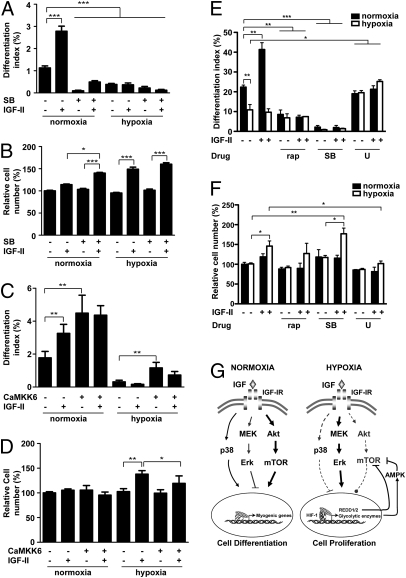
Fig. 5.
Hypoxia alters IGF action by suppressing p38 MAPK. (A and B) Inhibition of p38 MAPK activity by SB203580 (20 μM) abolishes myogenic action (A) but enhances mitogenic action (B) of IGF-II. Data are means ± SE, n =4–6. (C and D) Activation of p38 MAPK increases differentiation but inhibits proliferation. C2C12 cells were transfected with control plasmid or constitutively active MKK6 (CaMKK6) plasmid and induced to differentiate under normoxic or hypoxic conditions. At 24 h after differentiation was induced, differentiation index (C) and total cell number (D) were determined. Data are mean ± SE, n = 3. (E and F) Hypoxia converts myogenic action of IGF-II into mitogenic action in primary muscle cells. Primary murine skeletal myoblasts were induced to differentiate under normoxia or hypoxia with or without 100 nM rapamycin, 10 μM SB203580, or 10 μM U0126, and supplemented with or without IGF-II (400 ng/mL). At 14–21 h after induction of differentiation, cells were fixed and quantified for differentiation (E) and cell number (F). Data are mean ± SE, n = 3. (G) Schematic diagram illustrating mechanisms by which hypoxia specifies IGF actions. There are at least three signaling pathways downstream of the IGF1R: Akt-mTOR, p38 MAPK, and Erk1/2 MAPK in myoblasts. Activation of Akt-mTOR pathway strongly promotes myogenic differentiation (arrow) but has little effect on proliferation (circle). Activation of p38 MAPK promotes differentiation and inhibits proliferation (horizontal line). In contrast, activation of the Erk1/2 MAPK stimulates proliferation but inhibits differentiation. Under normoxia, binding of the IGF1R by IGF strongly activates the Akt-mTOR signaling pathway and p38 MAPK pathway (solid lines). Both Akt-mTOR and p38 MAPK positively contribute to myogenesis by up-regulating myogenic genes. IGF also activates Erk1/2 MAPK signaling, which results in a modest increase in cell number. Hypoxia alters cellular response to IGF signaling by suppressing Akt-mTOR and p38 MAPK signaling activities (broken lines). Hypoxia, through the activation of HIF-1, up-regulates REDD and several glycolytic enzymes expression, which inhibit Akt and mTOR activity. Under hypoxia, binding of the IGF-1R by IGF preferentially activates the Erk1/2 MAPK signaling pathway, which in turn stimulates cell proliferation and suppresses differentiation.