Figure 3.
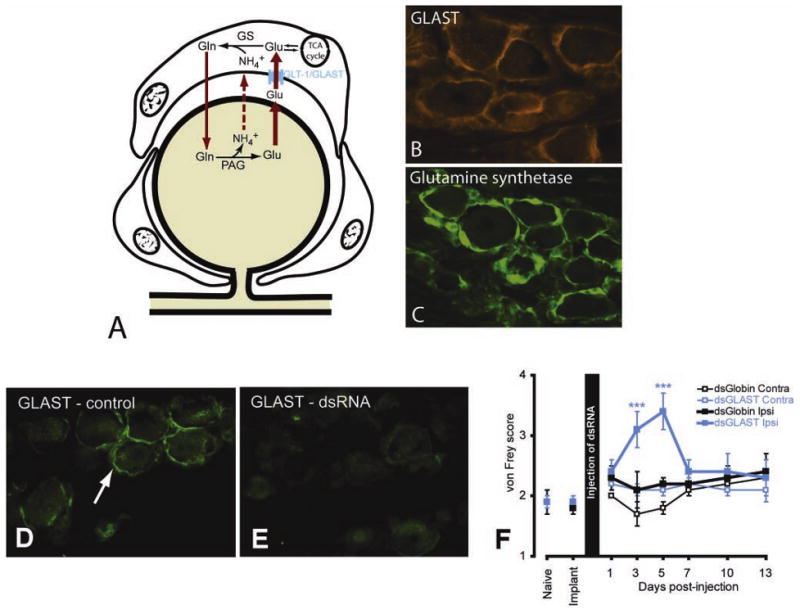
A, Diagram illustrating the role of satellite ganglion cells (SGCs) in glutamate recycling. The glial glutamate transporter (GLAST) transports extracellular glutamate (Glu) into the SGC where glutamine synthetase (GS) converts glutamate to glutamine (Gln), which is eventually recycled to the neuron for conversion into glutamate. In the trigeminal ganglion, SGCs express GLAST (B, red) and glutamine synthetase (C, green). D, GLAST immunostaining of SGC from a control ganglion (green, arrow). E, Five days following injection of GLAST dsRNA into the trigeminal ganglion there is an obvious reduction of GLAST immunostaining. F, von Frey scores for 13 days following injection of the dsRNAs into the trigeminal ganglion. There was an increase in von Frey scores for the GLAST dsRNA but no increase in von Frey score was observed for the control (globin) dsRNA, nor on the side contralateral to the injection. *** P < .001, compared with contralateral side.
