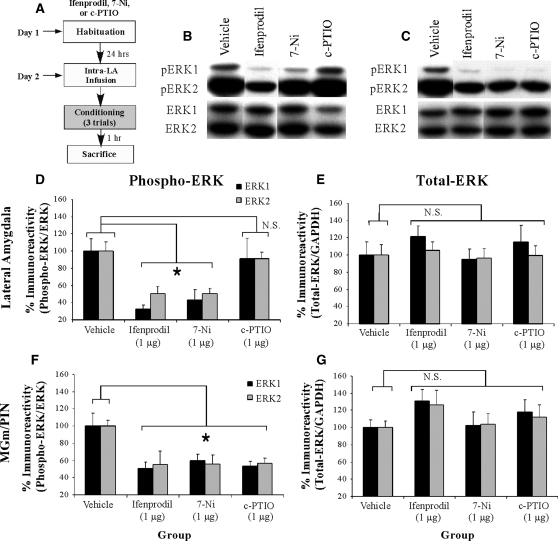
Figure 1.
Synaptic plasticity and NO signaling in the LA selectively regulate phosphorylation of ERK/MAPK in the LA and MGm/PIN following fear conditioning. (A) Schematic of behavioral protocol. Rats were given intra-LA infusion of the vehicle (n =8), the NR2B selective antagonist Ifenprodil (1 µg/side; n =8), the NOS inhibitor 7-Ni (1 µg/side; n =8), or the membrane impermeable NO scavenger c-PTIO (1 µg/side; n =8), followed 30 min later by fear conditioning. Rats were sacrificed 1 h following training. (B) Representative blots for both phospho-ERK (pERK) and total ERK in the LA. (C) Representative blots for both pERK and total ERK in the MGm/PIN. (D) Mean (± SEM) percent pERK immunoreactivity from LA punches taken from rats given intra-LA infusions of vehicle, Ifenprodil, 7-Ni, or c-PTIO. Here, pERK levels have been normalized to total ERK levels for each sample. (E) Mean (± SEM) percent total-ERK immunoreactivity from LA punches taken from rats given intra-LA infusions of vehicle, Ifenprodil, 7-Ni, or c-PTIO. Here, total ERK levels have been normalized to GAPDH levels for each sample. (F) Mean (± SEM) percent pERK immunoreactivity from MGm/PIN punches taken from the rats in D given intra-LA infusions of vehicle, Ifenprodil, 7-Ni, or c-PTIO. Here, pERK levels have been normalized to total ERK levels for each sample. (G) Mean (± SEM) percent total-ERK immunoreactivity from MGm/PIN punches taken from the rats in D given intra-LA infusions of vehicle, Ifenprodil, 7-Ni, or c-PTIO. Here, total ERK levels have been normalized to GAPDH levels for each sample. (*) P< 0.05 relative to vehicle-infused rats.