Fig. 2.
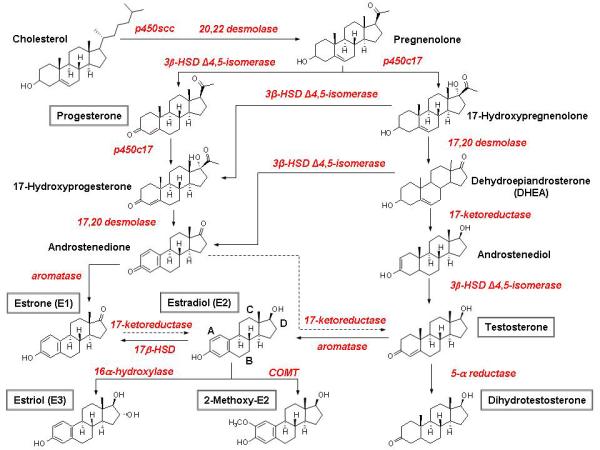
Ovarian Steroid Hormone Synthesis. In premenopausal women, the ovaries are the principal source of E2. The first, rate-limiting step in is the transfer of cholesterol from the cytosol to the inner membrane of the mitochondrion with the aid of StAR, and the conversion of cholesterol to pregnenolone. After side chain cleavage and utilizing the delta-5 or delta-4 pathway, androstenedione is the key intermediary. A fraction of androstenedione is directly “aromatized” to E1, which is subsequently converted to E2. Alternatively, androstenedione is converted to testosterone, which in turn undergoes conversion to E2 by aromatase. In postmenopause, the circulating steroids androstenedione, testosterone, and E1 become the major precursor substrates of E2 production in peripheral and estrogen target tissues.
