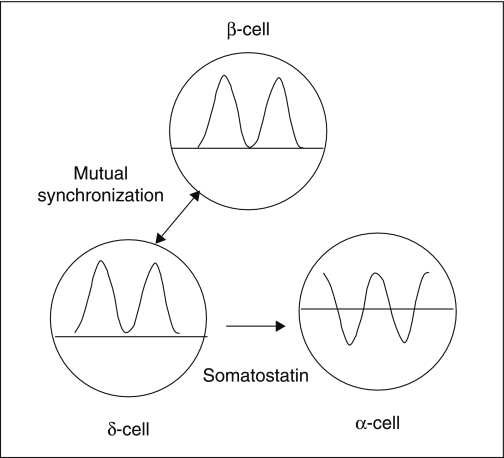
Figure 6.
Model of cell interactions important for glucose generation of pulsatile hormone release from an islet. Dotted lines indicate level of basal release before the rise of glucose. Glucose generates simultaneous pulses of insulin and somatostatin release by mutual synchronization of β- and δ-cells. The oscillations of glucagon appear in anti-synchrony and have nadirs below the basal level. Paracrine release of somatostatin from δ-cells accounts for the appearance of glucagon pulses 180° out of phase.