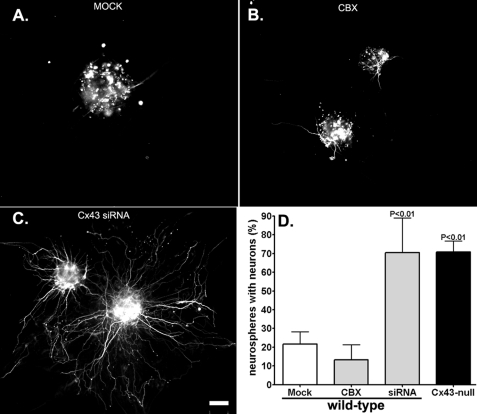
FIGURE 5.
Neuronal differentiation is independent of gap junction-mediated coupling. A–C, epifluorescence images showing β-III-tubulin-positive cells in mock transfected (A), CBX-treated (B), and Cx43 siRNA-transfected WT neurospheres (C). Note the presence of extensive neuronal neurite projections after knockdown of Cx43 with siRNA from WT neurospheres compared with CBX- and mock-treated neurospheres. Scale bar, 50 μm. D, bar histograms showing the mean ± S.E. (error bars) values obtained for the percent WT neurospheres with differentiated neurons (β-III-tubulin-positive cells with neurites) after 48-h treatment with transfection reagents (Mock), gap junction channel blocker CBX (100 μm), and after transfection with Cx43 siRNA. Knockdown of Cx43 with siRNA significantly increased the number of neurospheres with differentiated neurons to levels similar to those found in Cx43-null neurospheres; neither mock transfection nor CBX treatment altered the number of WT neurospheres with differentiated neurons. For knockdown efficiency, see supplemental Figs. 4S and 5S.