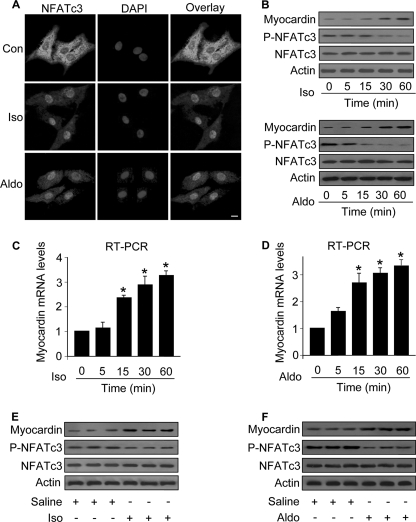
FIGURE 1.
Iso and Aldo induce an increase in myocardin expression levels and a decrease in the levels of phosphorylated NFATc3 in vitro and in vivo. A, Iso and Aldo induce NFATc3 redistributions from the cytoplasm to nuclei. The neonatal rat cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 μm Iso or 1 μm Aldo. 1 h after treatment the cells were collected for the analysis of NFATc3 by immunofluorescent staining. The cell nuclei were stained by 4′,6′-diamino-2-phenylindole (DAPI). Bar, 10 μm. B–D, the treatment with Iso and Aldo leads to an increase in myocardin expression levels and a decrease in the levels of phosphorylated NFATc3 (P-NFATc3). Cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 μm Iso or 1 μm Aldo. The cells were harvested at the indicated time for the analysis of myocardin protein levels, phosphorylated, and total NFATc3 levels by immunoblot (B) or myocardin mRNA levels by real time PCR (C and D). *, p < 0.05 versus control. E and F, Iso and Aldo treatment induces an elevation in myocardin levels and a reduction in the phosphorylated NFATc3 (P-NFATc3) in the animal model. C57BL/6 mice were infused with Iso or Aldo as described under “Experimental Procedures.” The levels of myocardin, P-NFATc3, and total NFATc3 in the hearts were analyzed by immunoblotting. A representative blot is shown. The data are expressed as the means ± S.E. of three independent experiments. Con, control.