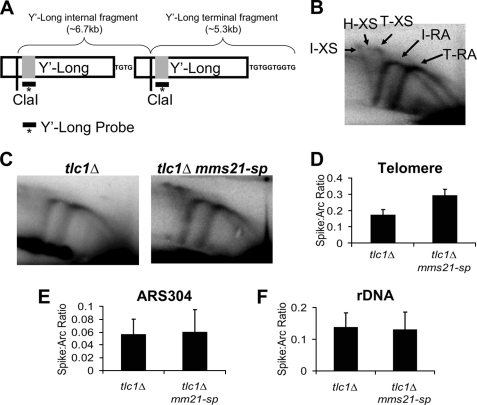
FIGURE 3.
Mms21 regulates the level of telomere recombination intermediates during senescence. A, example of the structure of a S. cerevisiae telomere showing Y′-Long elements and demonstrating the difference in fragment length between internal and terminal Y′-Long elements. Because of the existence of two distinct Y′-Long elements (internal and terminal), analysis of replication intermediates using the Y′-Long probe leads two distinct replication arcs (RA) and X-spikes (XS) being visualized during two-dimensional gel analysis. B, migration pattern of the RA and X-shaped molecules corresponding to the internal (I) and terminal (T) Y′-Long elements within two-dimensional gels are shown. The location of a hybrid (H) X-spike present in smc5/6 mutants is also indicated. C, representative two-dimensional gel analysis of replication intermediates accumulated in tlc1Δ and tlc1Δ mms21-sp strains at the telomere visualized with a probe specific for Y′-Long elements. D–F, comparisons of the ratio of X-shaped molecules to the replication arc within the telomere, near ARS304, and the rDNA locus for tlc1Δ and tlc1Δ mms21-sp mutants at 55 PD after spore germination. The respective p values are p < 0.05, p = 0.97, and p = 0.61 for differences between genotypes. Data represent the mean ± S.E. (error bars) of three to four independent samples/genotype.