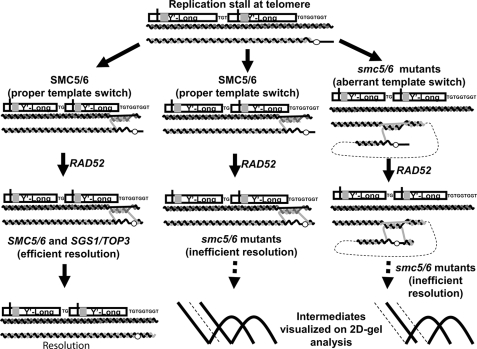
FIGURE 7.
Model depicting roles of the Smc5/6 complex at telomeres. During DNA replication, a damaged base or aberrant DNA structure leads to replication fork stalling and the initiation of template switch recombination to bypass the lesion. Smc5/6 helps ensure the proper selection of template and thus prevents abnormal linkages during the template switch. After replicating past the lesion using a complementary region of the sister chromatid, Rad52-dependent HR returns replication to the original parental template past the lesion. Smc5/6 along with Sgs1 and Top3 then assist in the resolution of the formed Rec-X recombination intermediate (left pathway). In the absence of a properly functioning Smc5/6 complex, telomeres remain linked preventing proper chromatid segregation (center pathway), and in addition are also more likely to use improper templates for template switch events (right pathway). An intrachromatid template switch is depicted, but aberrant events between sister chromatids or different chromosomes are also possible.