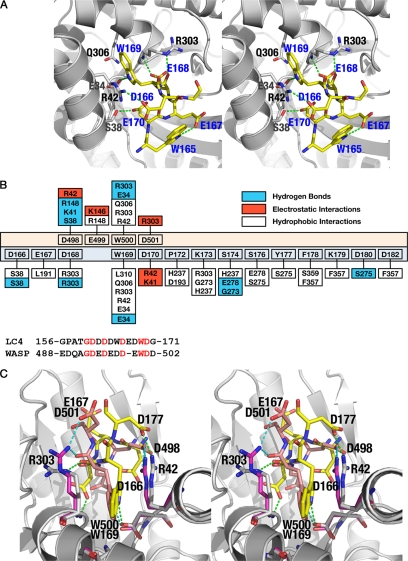
FIGURE 2.
Interaction of aldolase with the LC4 peptide of SNX9. A, the major interactions observed between the LC4 peptide and aldolase, common to all subunits in the asymmetric unit, is depicted. The aldolase subunit is shown as a schematic (gray) and the LC4 peptide represented as sticks (yellow). The residues of aldolase subunits involved in the LC4 interaction are also represented as sticks (gray). The residues corresponding to the LC4 peptide are labeled in blue, whereas those of aldolase are in black. B, top panel, shows the schematic representation of the interactions found between aldolase·SNX9 and aldolase·WASP complexes. The residues of the WASP peptide are depicted with peach background, whereas those of LC4 are pale cyan. The aldolase residues exhibiting hydrophobic (plain), electrostatic (red), and hydrogen bond (blue) interactions with either WASP or LC4 are also shown. Lower panel is the sequence alignment of the binding regions of LC4 and WASP peptides, showing the similarities and differences found around the tryptophan residue. Identical residues are in red. C, stereo image of the superposition of aldolase·SNX9 and aldolase·WASP complexes. The interactions observed between aldolase (gray) and the peptide LC4 (yellow) or WASP (peach) residues are shown by dotted lines.