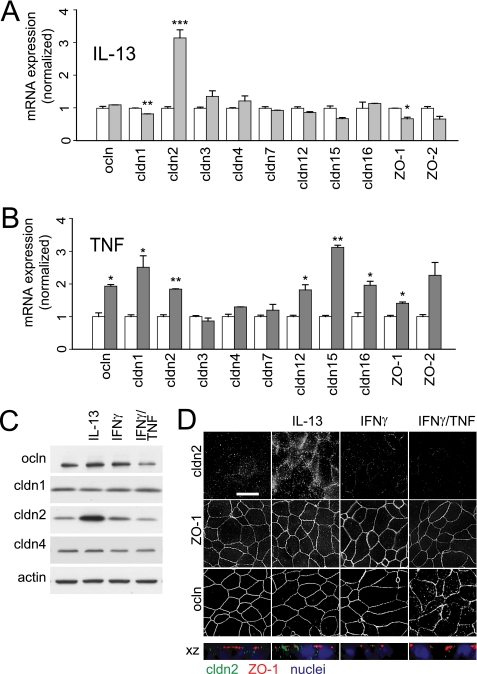
FIGURE 3.
TNF and IL-13 have unique effects on epithelial mRNA and tight junction protein expression. A, qRT-PCR shows a specific increase in claudin-2 mRNA after IL-13 treatment (0.1 ng/ml for 12 h; light gray bars). Data are normalized to identical monolayers not treated with IL-13 (white bars). B, qRT-PCR shows that TNF treatment (2.5 ng/ml for 4 h; dark gray bars) increases mRNA expression of occludin, ZO-1, and claudins-1, -2, -12, -15, and -16. Data are normalized to identical monolayers preincubated with IFNγ (2.5 ng/ml for 24 h) but not exposed to TNF (white bars). C, immunoblots show a 308 ± 58% increase in claudin-2 protein expression and 60 ± 18% reduction in occludin protein content after IL-13 or TNF treatment, respectively. Actin was used as a loading control. D, IL-13 increased claudin-2 localization at the tight junction and within peri-tight junction cytoplasmic vesicles, but did not affect occludin or ZO-1 distribution. In contrast, TNF caused occludin internalization but had no effect on claudin-2 expression or localization. ZO-1 distribution was not affected by either cytokine. Bar, 10 μm (*, p ≤ 0.05; **, p ≤ 0.01, S.E.).