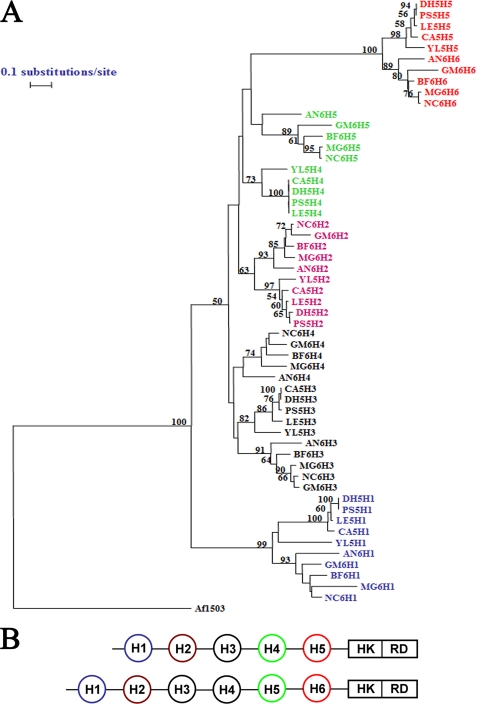
FIGURE 6.
Phylogenetic analysis of HAMP domains. A, phylogenetic tree. Individual HAMP domain sequences from the NIK1 orthologs having five HAMP domains from Yarrowia lipolytica (Q6C775_YARLI), Lodderomyces elongisporus (A5E5X7_LODEL), P. stipitis (A3LYT9_PICST), D. hansenii (DhNik1p; Q6BH10_DEBHA), and C. albicans (CaNik1p; Q9URL9_CANAL) were obtained from SMART data base. YL5H1, YL5H2, YL5H3, YL5H4, and YL5H5 were HAMP domains from Y. lipolytica ortholog. They were named serially according to their position in the protein from N terminus. Similarly, LE5H1, LE5H2, LE5H3, LE5H4, and LE5H5 were from L. elongisporus; PS5H1, PS5H2, PS5H3, PS5H4, and PS5H5 were from P. stipitis; DH5H1, DH5H2, DH5H3, DH5H4, and DH5H5 were from D. hansenii; CA5H1, CA5H2, CA5H3, CA5H4, and CA5H5 were from C. albicans. Representative orthologs of NIK1 containing six HAMP domains are B. fuckeliana (Q8X1E7_BOTCI), Gibberella moniliformis (Q6SLB2_GIBMO), N. crassa (Nik1p; Q01309_NEUCR), M. grisea (Q9C1U1_MAGGR), and Aspergillus niger (A2QP39_ASPNG). BF6H1, BF6H2, BF6H3, BF6H4, BF6H5, and BF6H6 are individual HAMP domain sequences (named serially according to their position from N terminus) from ortholog in B. fuckeliana. Similarly, GM6H1, GM6H2, GM6H3, GM6H4, GM6H5, and GM6H6 were from G. moniliformis; NC6H1, NC6H2, NC6H3, NC6H4, NC6H5, and NC6H6 were from N. crassa; MG6H1, MG6H2, MG6H3, MG6H4, MG6H5, and MG6H6 were from M. grisea; AN6H1, AN6H2, AN6H3, AN6H4, AN6H5, and AN6H6 were from A. niger. Amino acid sequences of the individual HAMP domains were compared using the Clustal_X program (supplemental Table 2 and supplemental Fig. 1). Aligned sequences were analyzed by using the TREECON software package. A neighbor-joining tree (50% or more boot strap values of 1000 replicates are indicated) is shown. HAMP domain sequence from Archaeoglobus fulgidus protein Af1503 (30) was included as out-group. B, schematic showing Nik1 orthologs carrying five HAMP domains and six HAMP domains. Similarly colored HAMP domains from either group are clustered together in the phylogenetic tree. HK, histidine kinase; RD, receiver domain.