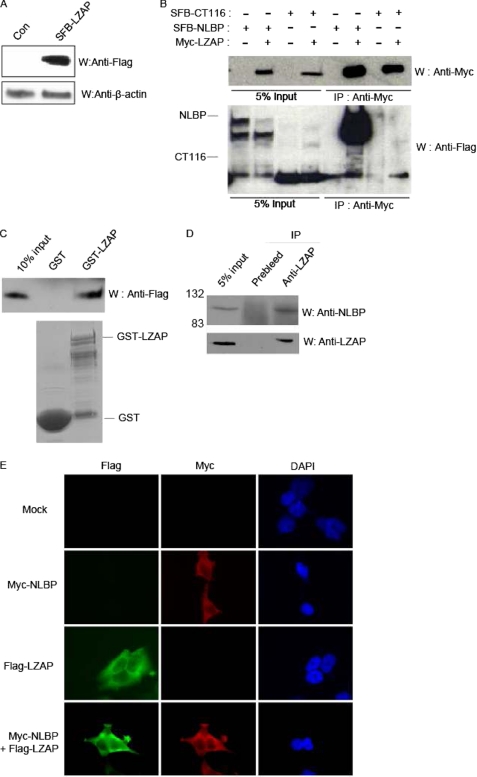
FIGURE 1.
Identification of NLBP as a novel LZAP-binding protein. A, establishment of human embryonic kidney 293T cell lines stably expressing SFB-LZAP. Cell extracts prepared from 293T cells stably expressing a control (Con) plasmid or SFB-LZAP fusion protein were subjected to Western blotting analysis (W) using anti-FLAG antibody. B, interaction between exogenous Myc-tagged LZAP and SFB triple-tagged NLBP or CT116. Immunoprecipitation (IP) reactions were performed using anti-Myc antibody and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-Myc and anti-FLAG antibodies. C, GST pulldown assay. GST only or GST-LZAP protein was incubated with cell lysates containing exogenously expressed SFB triple-tagged wild type NLBP (SFB-NLBP). After extensive washing, bound NLBP proteins were analyzed by Western blotting analysis with anti-FLAG antibody. The amounts of GST and GST-LZAP are shown in the lower panel. D, binding between endogenous LZAP and NLBP. Immunoprecipitation reactions were performed using preimmune serum or anti-LZAP antibodies and subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-NLBP (upper panel) or anti-LZAP (lower panel) antibody. E, colocalization of NLBP with LZAP. 293T cells were transfected with Myc-tagged NLBP and SFB triple-tagged LZAP expression plasmids. Next, immunofluorescence assays were performed using anti-FLAG and -Myc antibodies. 4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was used as an indicator for the nucleus. Mock, mock-transfected.