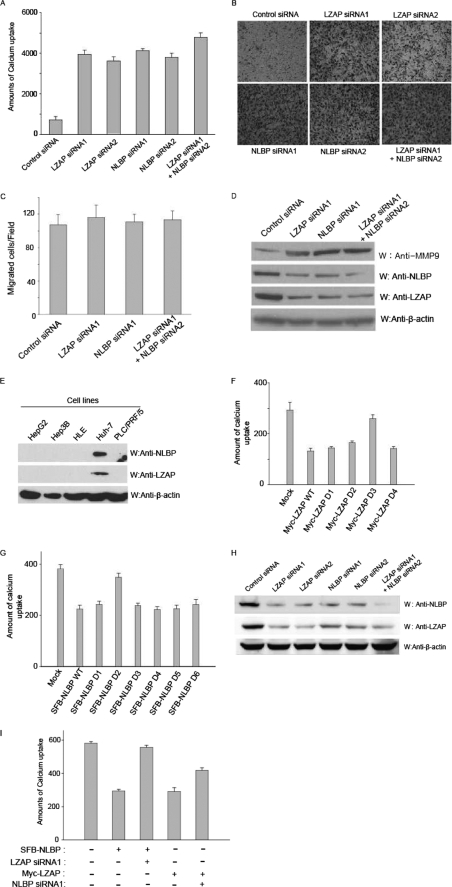
FIGURE 4.
NLBP is important for inhibition of cell invasion. A, B, C, D, and H, control, LZAP, NLBP, or LZAP + NLBP siRNAs were transfected into U2OS cells. Invasion assays using the transfected U2OS cells were performed using the calcium uptake method (A) or the Matrigel assay (B). These experiments were performed in duplicate, and the results shown are the average of three independent experiments. S.D. is shown on each bar. C, down-regulation of LZAP or NLBP expression did not affect cellular migration through the Transwell permeable supports in the absence of Matrigel. The migration assay was performed in the absence of Matrigel using U2OS cells transfected with control, LZAP, NLBP, or LZAP + NLBP siRNAs. D, MMP-9 expression levels were increased following knockdown of LZAP or NLBP, as shown by Western blot analysis (W) with control, LZAP, NLBP, or LZAP + NLBP siRNA-transfected U2OS cells. E, NLBP and LZAP protein expression levels in hepatocellular carcinomas. The lysates of various hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines were subjected to immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. F and G, identification of the LZAP and NLBP regions important for cell-invasive activity. Hep3B cells were transfected with plasmids encoding Myc-LZAP or serial deletion mutants (F) (D1–D4) or wild type SFB-NLBP (WT) or serial deletion mutants (G) (D1–D6). Calcium uptake was measured to assay for invasive activity. These experiments were performed in duplicate, and the results shown are the average of three independent experiments. S.D. is shown on each bar. Mock, mock-transfected. H, treatment with LZAP or NLBP siRNA can efficiently down-regulate both LZAP and NLBP expression. Expression levels of endogenous LZAP and NLBP proteins in LZAP or NLBP siRNA-transfected U2OS cells were confirmed using the indicated antibodies. I, both NLBP and LZAP proteins are needed to inhibit cell invasion. As indicated, control or LZAP or NLBP expression plasmids and LZAP or NLBP siRNAs were transfected into Hep3B cells, and invasion assays were performed using the calcium uptake method. These experiments were performed in duplicate, and the results shown are the average of three independent experiments. S.D. is shown on each bar.