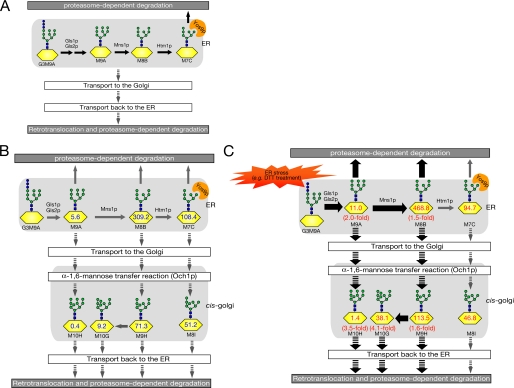
FIGURE 7.
Predicted scheme for overall N-glycan processing on misfolded glycoproteins subjected to ERAD. A, a current model for N-glycan processing in glycoprotein ERAD (14). N-Glycans on misfolded glycoproteins are further trimmed by glucosidases (Gls1p and Gls2p) and mannosidases (Mns1p and Htm1p), which can generate M7C glycan. Yos9p, a lectin-like ERAD component, recognizes the α-1,6-terminal mannose residue of M7C. Several misfolded glycoproteins may traffic between ER and Golgi before their degradation, as depicted by downward arrows. B, hypothetical scheme of N-glycan processing on misfolded glycoproteins, based on our fOS analysis. The numbers (pmol/10 mg protein) on N-glycans are based on fOSs analysis in ams1Δ cells. C, when UPR is induced by DTT, yeast cells facilitate the generation of M8B glycans on misfolded proteins and transport misfolded glycoproteins to the Golgi. Thick arrows indicate pathways up-regulated by UPR.