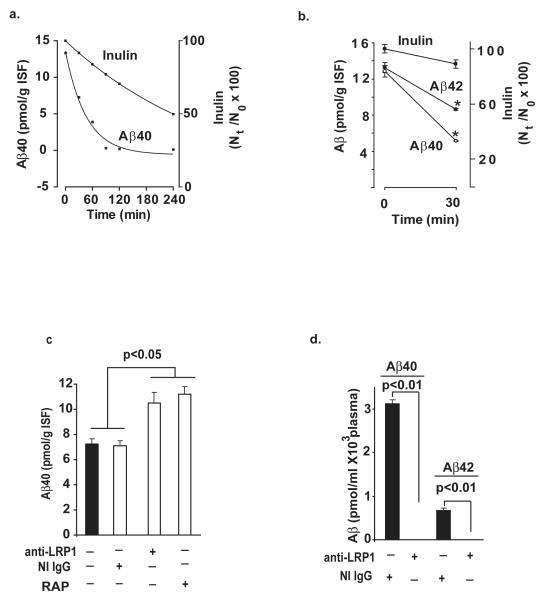
Fig. 2.
a, Time-disappearance curves of unlabeled human Aβ40 (0.0866 ng) and 14C-inulin from brain ISF after their simultaneous administration into the caudate nucleus in mice. Each pair of time points represents data from individual mice for Aβ and inulin. b, Clearance of unlabeled human synthetic Aβ40 and Aβ42 from brain ISF within 30 min of administration into the caudate nucleus. Aβ40 and Aβ42 were infused simultaneously with 14C-inulin. c, Levels of Aβ40 in brain after 30 min of its simultaneous administration with inulin (not shown) in the presence and absence of anti-LRP1 (N-20, 60 μg/mL), non-immune IgG (60 μg/mL) and RAP (5 μM). d, Intact human unlabeled Aβ40 and Aβ42 in plasma 30 min after local CNS administration of peptides simultaneously with 14C-inulin in the presence and absence of centrally administered anti-LRP1 (N-20, 60 μg/mL). Inulin levels were barely detectable (not shown). Aβ levels were determined focally in brain and plasma by using human specific ELISAs, as described in Methods. In b-d, values are mean ± s.e.m. from 3 to 5 independent experiments.