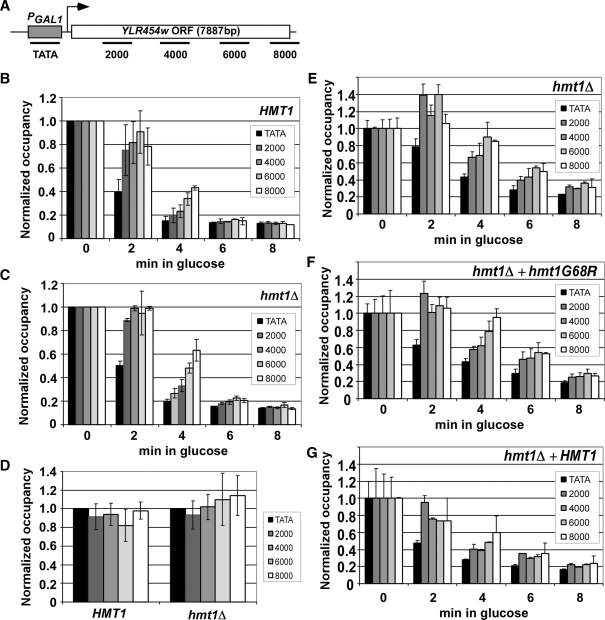
Figure 2.
hmt1Δ reduces the rate of transcription elongation in vivo. (A) Diagram of the PGAL1-YLR454w gene with positions of PCR primers indicated (in bp) from nucleotide A of the start codon. (B, C) Quantification of Rpb3p occupancy measured by ChIP with antiRpb3p antibodies at the five positions across PGAL1-YLR454w indicated in (A) for HMT1 (CMY125) (B) or hmt1Δ (CMY130) (C). Cells grown in YP containing galactose were treated with 4% glucose for the indicated times. DNA extracted from immunoprecipitates and input chromatin samples was amplified by PCR in the presence of [33P]dATP for the different regions of PGAL1-YLR454w, together with a fragment from a non-transcribed region of Chr I to control for non-specific immunoprecipitation. PCR products were quantified with by phosphorimaging and ratios of experimental-to-control signals in the immunoprecipitates were normalized for the corresponding ratios for input samples to yield the occupancy values. Occupancies were normalized to those derived from cells grown in 2% galactose for 2 h (time = 0). (D) hmt1Δ does not detectably affect RNAP II processivity in vivo. HMT1 and hmt1Δ cells were grown in galactose medium (time = 0) and quantification of Rpb3p occupancy was performed as above. The value at each position was normalized to that of the WT strain. (E−G) Methyltransferase activity of Hmt1p stimulates the rate of transcription elongation in vivo. hmt1Δ cells containing empty vector (E) or plasmids harboring hmt1-G68R (F) or HMT1 (G) were induced with SC-LEU 2% galactose for 2 h (time = 0) and treated with 4% glucose for the indicated times. ChIP analysis of Rpb3p across the PGAL1-YLR454w gene was conducted as described earlier. Average results obtained from two independent cultures and two PCR amplifications for each culture were plotted in the histograms.