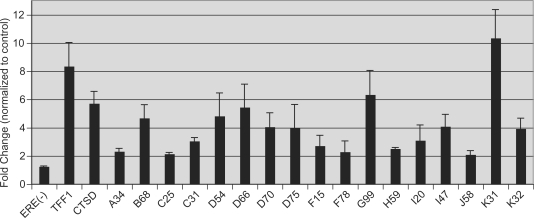
Figure 1.
ChIP-PCR validation of ERα-bound loci. ERα-bound loci determined by ChIP-on-chip were interrogated for E2-dependent ERα binding using quantitative ChIP-PCR (for genomic coordinates see Table 2). MCF7 cells were treated with E2 (100 nM) or vehicle (EtOH) for 45 min. ChIP was performed using antibodies against ERα. Quantitative PCR using genomic primers employed the 28S rRNA coding sequence as internal reference. Shown are E2-treated values normalized to control values. ERα was not recruited to an ERE-less and ChIP-on-chip negative locus dubbed ERE(–). Similar studies using genomic PCR primers for the known E2-responsive genes TFF1 and CTSD demonstrated rapid recruitment of ERα to these enhancer regions in response to E2. ChIP-PCR targeting 17 additional loci similarly revealed E2-dependent enrichment (>2-fold) of ERα at all sites. Values are the average of three experiments with SEM. Oligonucleotide sequences are presented in Supplementary Table S1.