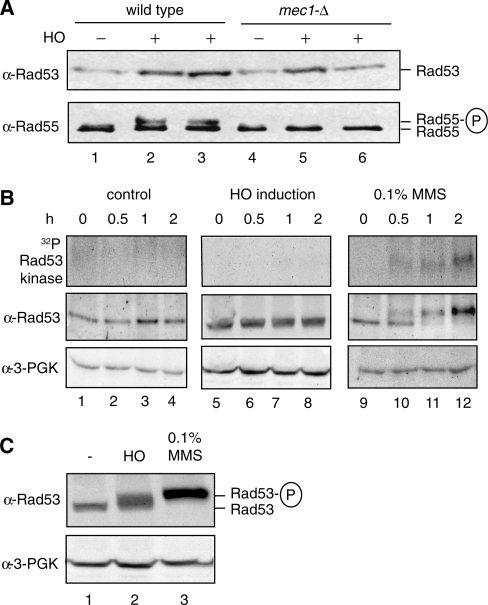
Figure 3.
Rad55-S378 is phosphorylated after HO-mediated DSB induction in G1-arrested cells in the absence of detectable Rad53 activation. (A) Mec1 controls Rad55-S378 phosphorylation in G1-arrested cells. Rad55 was immunoprecipitated from equal amounts of cell extracts of G1-arrested wild-type (WDHY2172: lanes 1–3) or mec1-Δ (WDHY2173: lanes 4–6) cells after HO-endonuclease had been induced (lanes 2, 3, 5, 6) or not (lanes 1, 4) and analyzed by immunoblotting (lower panel). Rad53 was analyzed by immunoblotting in total cell extracts (upper panel). The apparent variation in the Rad53 protein level is not systematic and likely without significance. (B) Rad53 is not detectably activated in response to a single DSB during G1-arrest in wild-type cells (WDHY2172). Samples were taken from cultures of untreated cells (control: lanes 1–4), after induction of HO endonuclease (HO induction: lanes 5–8) and after addition of 0.1% MMS (lanes 9–12) at indicated times after G1 arrest was established by addition of α-factor. The upper panels show in situ Rad53 activity assays. In the middle panels, Rad53 was analyzed by immunoblotting of total cell extracts. The lower panels show corresponding loading controls. (C) Rad53 is activated in response to a single DSB in cycling wild-type cells (WDHY2172). Samples were taken from cycling cultures of untreated cells (lane 1), cells with one DSB inflicted by HO endonuclease (lane 2) and MMS-treated cells (lane 3) after 2 h of treatment. The upper panel shows the Rad53 immunoblot and the lower panel the corresponding loading controls (B).