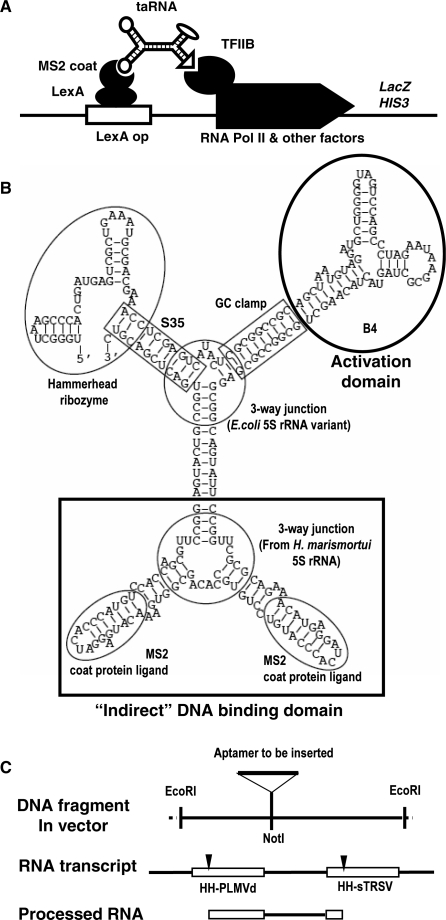
Figure 2.
Molecular and genetic design of taRNA. (A) Schematic diagram showing the function of the taRNA. (B) The most stable structure of the taRNA as predicted by mfold. Each structural and functional unit is indicated by a circle or a rectangle, with the name of the element next to it. The three-way junction connecting the two MS2 coat protein ligands was derived from the 5S rRNA of H. marismortui (47). The other three-way junction was a stable 5S rRNA variant named ‘System F’ (48). (C) Schematic diagram depicting the EcoRI segment in the pDB series of plasmids before and after subcloning, and the RNA transcribed from the synthetic gene before and after further processing by hammerhead ribozyme cleavage. The DNA and RNA segments are aligned to show their relationship. The two ribozymes were taken from peach latent mosaic viroid (PLMVd) and tobacco ringspot virus satellite RNA (sTRSV), respectively (31). The cleavage sites of the ribozymes are indicated by arrowheads.