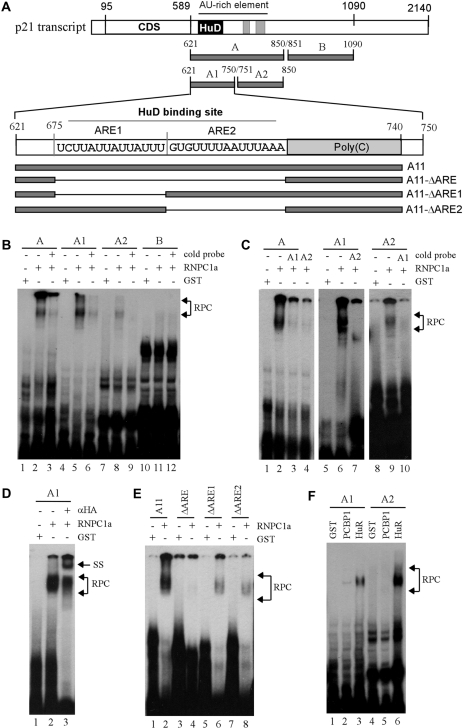
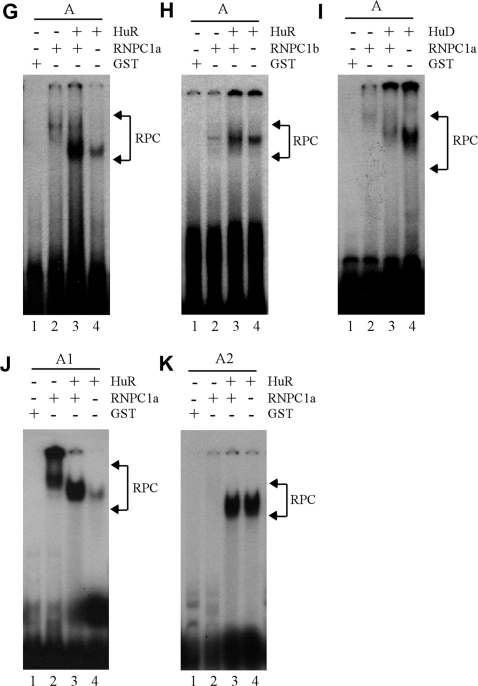
Figure 5.
Identification of AREs as a RNPC1-binding site in p21 3′-UTR. (A) Schematic presentation of p21 3′-UTR along with the location of AREs, poly(C)-rich region, HuD-binding site and RNA probes used for REMSA. (B) REMSA was performed by mixing 32P-labeled probe A, A1, A2, or B with recombinant GST or GST-HA-RNPC1a. An excess amount of unlabeled cold probe was used for competition in lanes 3, 6, 9 and 12. (C) The experiment was performed as in (B) except probes used. For competition assay, an excess amount of unlabeled cold probe (A1 or A2) was added to a reaction mixture containing RNPC1 and probe A, A1 or A2. (D) For supershift assay, 3 µg of anti-HA antibody was added to a reaction mixture containing probe A1 and GST-HA-RNPC1. (E) The experiment was performed as in (B) except probes used. (F) HuR has a higher affinity to probe A2 than A1 whereas PCBP1 only weakly binds to probe A1. The experiment was performed with GST-tagged HuR or PCBP1 mixed with 32P-labeled probe A1 or A2. (G and H) RNPC1 cooperates with HuR to bind p21 transcript. GST-tagged RNPC1a or RNPC1b was mixed with GST-tagged HuR and 32P-labeled probe A for REMSA analysis. (I) RNPC1 inhibits the binding of HuD to p21 transcript. The experiment was performed as in (G–H) except that GST-tagged HuD was used. (J and K) The experiments were performed as in (G) except the probes used.