Figure 1.
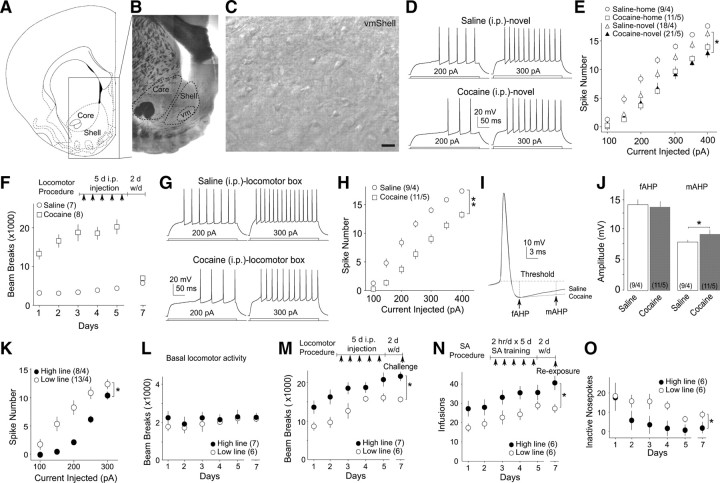
The intrinsic membrane excitability of NAcSh MSNs was decreased after 2 d withdrawal from 5 d intraperitoneal cocaine injections either within the home cages or in a novel environment. A, A diagram showing the NAc shell and core. B, An example brain slice at a low magnification (through the 4× objective) in which the dashed circles indicate the operationally defined core and shell regions as well as the ventral-medial region (vm) of the shell. C, Example image at a high magnification (40×) showing MSNs within the ventral-medial regions of the shell of the NAc. Scale bar, 20 μm. Images in B and C were taken from the fresh tissue through the same microscope-imaging system used for identifying and recording NAcSh MSNs throughout the present study. D, Examples showing action potentials elicited by 200 and 300 pA current steps in two example NAcSh MSNs from rats receiving novelty-paired injections of saline and cocaine, respectively. E, Summarized data showing that 2 d withdrawal from repeated intraperitoneal injections of cocaine, either within the home cages or in the novel environment, decreased the intrinsic membrane excitability of NAcSh MSNs. F, Summarized data showing that rats receiving a 5 d procedure of intraperitoneal cocaine injection (diagrammed in the inset) exhibited sensitized locomotor responses. On day 7 (2 d withdrawal), the spontaneous locomotor activity was similar in both groups of rats. G, Examples showing evoked action potentials in two NAcSh MSNs from a saline-pretreated and a cocaine-pretreated rat in F. H, Summarized data showing that 2 d withdrawal from the locomotor sensitization procedure significantly decreased the membrane excitability of NAcSh MSNs. I, The averaged AHPs from all recorded MSNs from saline- and cocaine-pretreated rats. J, Summarized data showing that the mAHP, but not fAHP, was increased in cocaine-pretreated rats. K–M, Summarized data showing that, between the two breeding lines of Long–Evans rats (high and low lines), the high line rats exhibited lower membrane excitability in NAcSh MSNs (K) and higher cocaine-induced locomotor response (M), whereas the basal locomotor activity was similar in these two lines of rats (L). N, Summarized data showing differential acquisition of cocaine SA between high line and low line rats. O, Summarized data showing that high line and low line rats exhibited different numbers of inactive nose pokes during the acquisition of cocaine SA. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01.