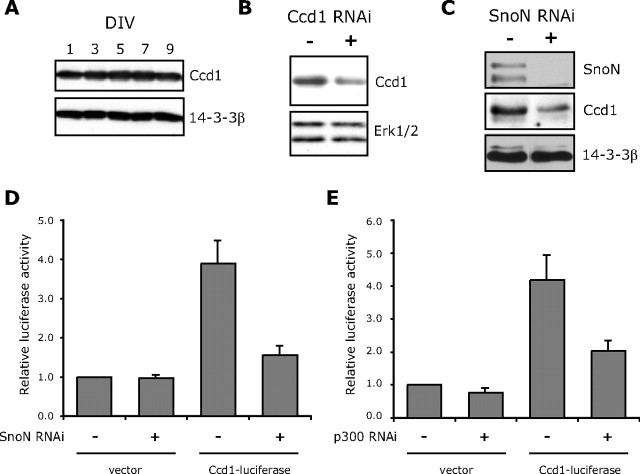
Figure 3.
Identification of Ccd1 as a SnoN-regulated downstream target gene. A, Lysates of granule neurons cultured for the indicated DIV were immunoblotted with the Ccd1 or 14-3-3β antibody. Cultured days in vitro are indicated. B, Lysates of granule neurons transfected by nucleofection method with the Ccd1 RNAi plasmid (pSuper/ccd1i) or control pSuper plasmid were immunoblotted with the Ccd1 or ERK1/2 antibody. Ccd1 RNAi reduced the Ccd1-immunoreactive band, specifically. C, Lysates of granule neurons transfected by nucleofection with the SnoN RNAi (U6/snoni) or control U6 plasmid were immunoblotted with the SnoN, Ccd1, or 14-3-3β antibody. SnoN knockdown triggered downregulation of Ccd1 protein in neurons. D, Granule neurons were transfected with the SnoN RNAi (U6/snoni) or control U6 plasmid together with the Ccd1–luciferase reporter or the control vector pGL3basic and the EF renilla reporter, the latter serving as an internal control for transfection efficiency. The level of Ccd1–luciferase reporter gene expression was significantly reduced in SnoN knockdown neurons compared with control-transfected neurons (ANOVA; p < 0.01; n = 3). E, Granule neurons were transfected with the p300 RNAi (U6/p300i1) or control U6 plasmid together with the Ccd1–luciferase reporter or the control vector pGL3basic and the EF renilla reporter, the latter serving as an internal control for transfection efficiency. The level of Ccd1–luciferase reporter gene expression was significantly reduced in p300 knockdown neurons compared with control-transfected neurons (ANOVA; p < 0.05; n = 3).