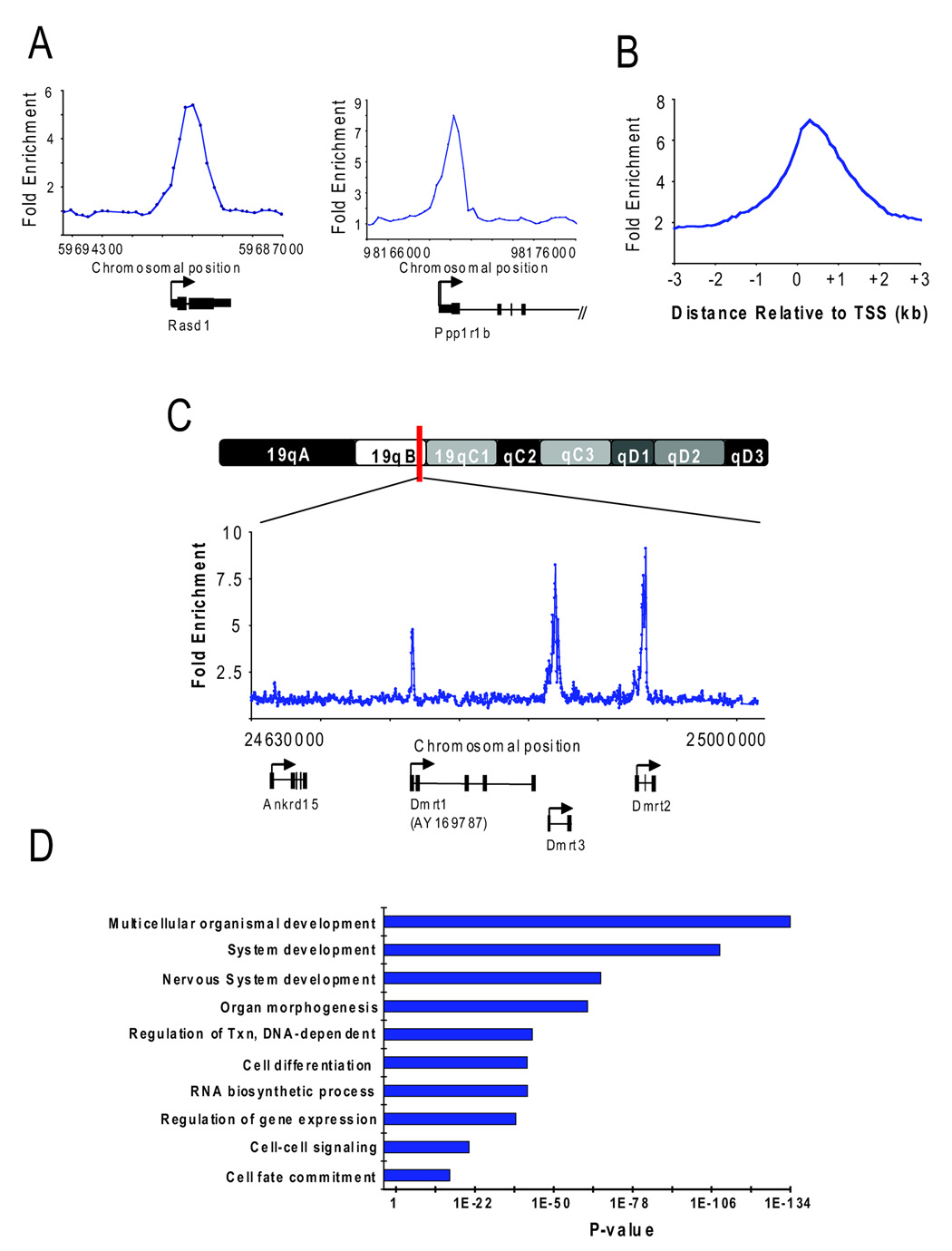
Figure 1. H2AZ occupies promoter regions in ES cells.
(A) Representative examples of DNA sequences occupied by H2AZ isolated using chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and promoter microarrays. ChIP with core histone H3 was hybridized together with H2AZ to control for nucleosome density. Note that hybridization of H2AZ ChIP-DNA with bulk chromatin as input yielded highly similar results in a replicate set of experiments. The plots show unprocessed enrichment ratios (blue) for all probes within a genomic region. Chromosomal positions are from NCBI build 34 (mm6) of the mouse genome. Genes are shown to scale below plots. The start and direction of transcription are both indicated by an arrow. (B) Distribution of the distance between bound probes and the closest transcription start site (TSS). Data are the average unprocessed enrichment ratios for each oligonucleotide probe within the –4 kb to +4 kb genomic region for all enriched genes. (C) Representative example of DNA sequences occupied by H2AZ using ChIP and tiled chromosome 19 microarrays. The plots show unprocessed enrichment ratios (blue) for all probes within a genomic region (ChIP versus histone H3). Genes are shown to scale below plots as in (A). (D) Gene ontology analysis for biological process of H2AZ-enriched genes. Ontology terms are represented on the y-axis and the p-value for enrichment of bound genes relative to all genes represented on the microarray is shown for each category on the x-axis.