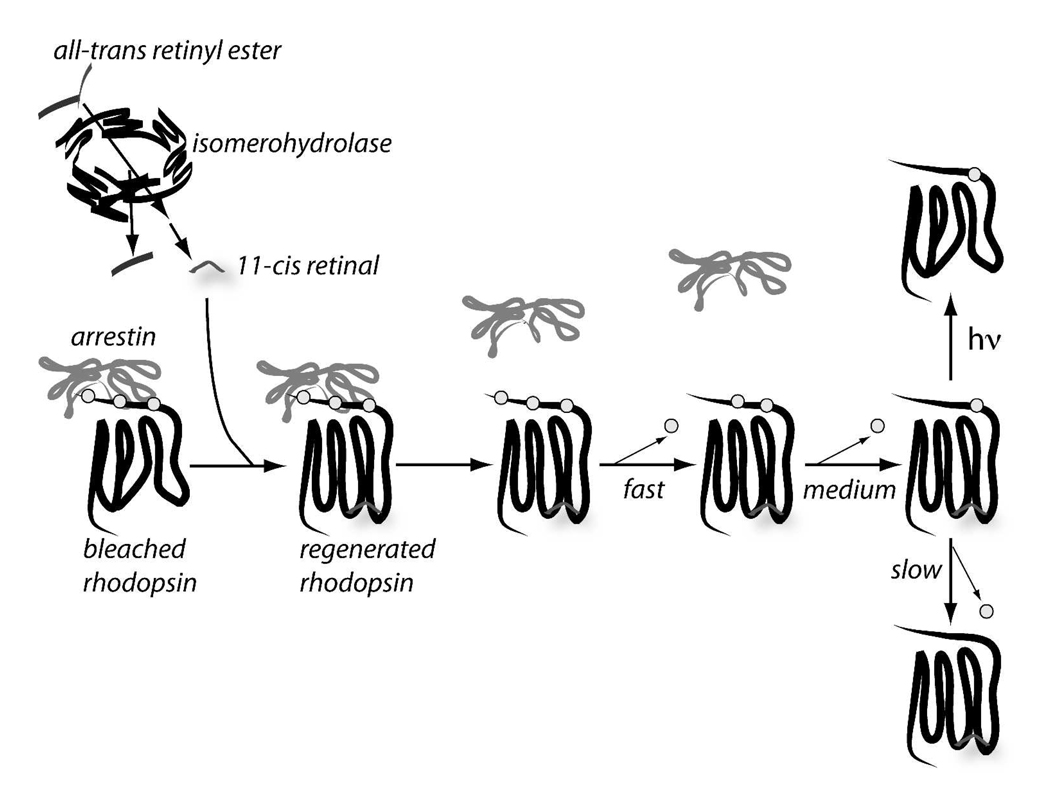
Fig. 9. Schematic model of the steps leading to dephosphorylation of rhodopsin.
Isomerohydrolase activity produces 11-cis retinal, which then regenerates rhodopsin that is phosphorylated and complexed with arrestin. Regeneration releases arrestin so that rhodopsin dephosphorylation can proceed. During bright illumination some regenerated rhodopsin can be bleached before it is completely dephosphorylated.