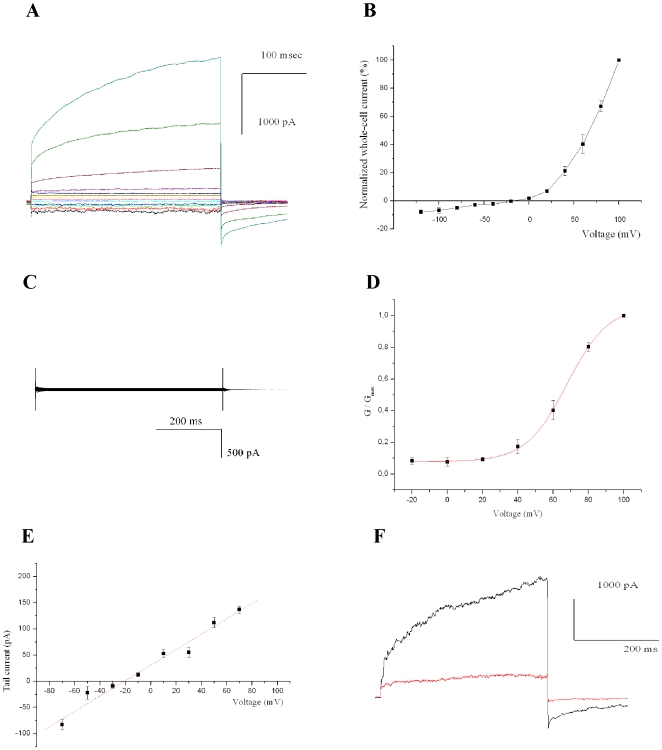
Figure 3. SynK functions as a potassium channel in CHO cells.
A) Representative whole-cell currents in a pSynK-EGFP-transfected fluorescent cell, elicited by application of voltage steps of 300 ms duration, from −140 to + 100 mV in 20-mV steps, from a holding potential of −50 mV. Pulses were applied every 45 seconds, allowing complete deactivation of the channel. Different colours refer to different applied voltages. B) Current-voltage relationship. Peak currents normalized to current measured at +100 mV (n = 6, SEM values are reported). C) as in A), but from a control, pEGFP-N1-transfected cell. D) Boltzman fit of G/Gmax (n = 6). E) Determination of selectivity from tail currents, elicited by stepping voltage for 400 ms to +60 mV, followed by application of −100 to + 100 mV in 20-mV voltage steps for 400 ms. Tail currents are reported as function of voltage. Reversal potential is −21±4 mV (n = 4). In A) to E) bath and pipette solutions contained 150 mM NaCl, 70 mM KCl and 134 mM KCl, respectively. F) Current recorded in K+-gluconate solution at +100 mV, before (black) and after (red) addition of 15 mM Cs+ to bath. Results are representative of 4 experiments.