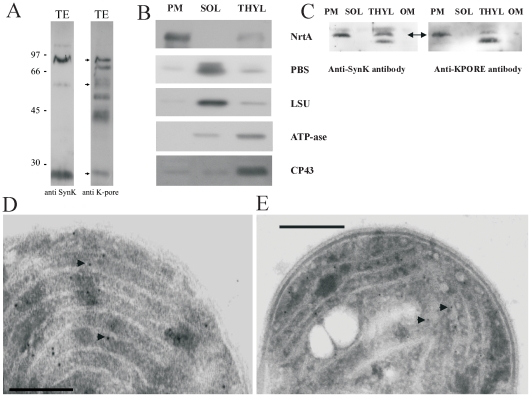
Figure 4. Localization of SynK in Synechocystis.
A) Whole-cell cyanobacterial lysates containing 0.1 µg chlorophyll/lane were loaded on SDS-PAGE without urea and blotted with anti-SynK (1∶2500 dilution) (lane 1) and anti-KPORE (1∶10000) (lane 2) polyclonal antibodies. Apparent MWs of monomer, SDS-resistant dimer trimer and tetramer forms correspond to 26, 52, 76 and ca. 110 kDa. The anti-KPORE antibody, as expected, given the predicted presence of various potassium channels in this organism, recognized other proteins as well (lane 2). B) Plasmamembrane (PM), soluble (SOL) and thylakoid membrane (THYL) fractions were isolated from Synechocystis. The resulting fractions were checked for purity by using antibodies against markers of the plasmamembrane (NrtA), of the soluble fraction (PBS: allophycocyanin; LSU: large subunit of Rubisco) and of Thylakoid (ATP-ase and CP43). Cross-contamination to small extenct can be observed. 20 µg of proteins/lane. C) The obtained fractions were assayed for SynK content by using anti-SynK (left panel) and anti-KPORE (right panel) antibodies. 20 µg of proteins loaded/lane. The apparent MWs of the observed bands are 26 kDa (arrow) in the PM fraction and 26 and 24.5 kDa in the THYL fraction. D) Anti-SynK antibody used for immunogold electron microscopy confirms location of SynK protein in thylakoids (white membraneous structures). Arrows emphasize some of the gold particles. Bar: 200 nm. E) As control, anti-CP43 was used. Bar: 500 nm.