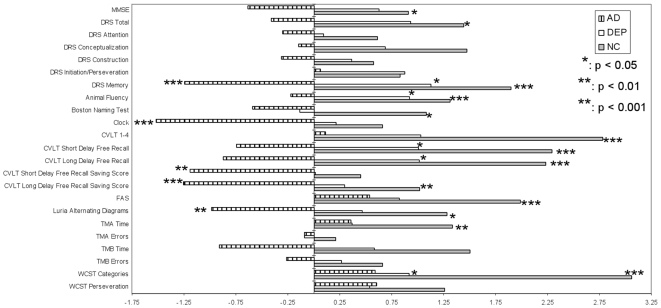
Figure 1. Comparison of Cognitive Performances of Patients with Alzheimer's Disease, Depressive Disorder, or Normal Cognition to those with Late-Life Schizophrenia.
Cohen's effect sizes have been calculated and plotted for the different cognitive tests comparing performances of patients with AD, DEP, or NC to those with LLS (who constitute the reference group). Positive effect sizes indicate that patients with AD, DEP, or NC perform numerically better than patients with LLS. Negative effect sizes indicate that the opposite. * indicates that the difference is statistically significant (p<0.05) after correcting for multiple comparisons. ** indicates that the difference is statistically significant (p<0.01) after correcting for multiple comparisons. *** indicates that the difference is statistically significant (p<0.001) after correcting for multiple comparisons. AD: Alzheimer's disease; Clock: Clock drawing test – Freedman scale; CVLT: California Verbal Learning Test II- Short Form; DEP: depressive disorder; DRS: Dementia Rating Scale-2; FAS: FAS Letter Fluency; MMSE: LLS: late-life schizophrenia; Mini-Mental Status Examination; NC: normal cognition; TMA and TMB: Trail Making Test A and B, respectively; WCST: Wisconsin Card Sorting Test – 64.