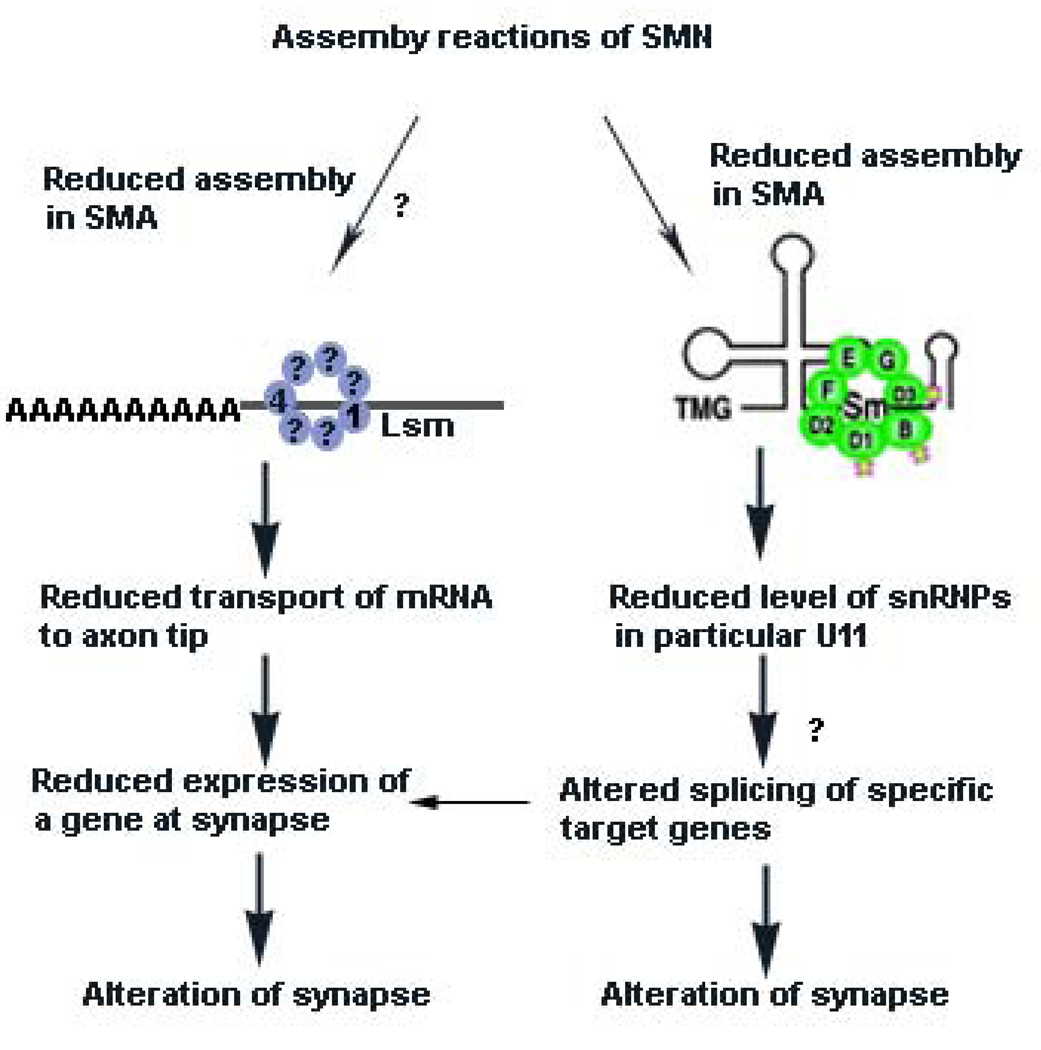
Figure 3. Mechanisms proposed to explain how reduced SMN levels cause SMA.
According to one hypothesis, reduced SMN levels result in reduced assembly of Sm proteins onto snRNA. This unevenly alters the levels of specific endogenous snRNPs, such as those used to splice minor introns (particularly U11) from pre-mRNA.40, 56, 104 It remains to be determined what the downstream target genes of the affected snRNPs are and how this specifically affects motor neuron function (indicated by a question mark (?)). One possibility is that the critical target gene is specific to motor neuron system. Alternatively, a function of critical importance to motor neurons could be disrupted.
In addition, it has been suggested that reduced levels of β-actin mRNA or other mRNA occur at the axon tip or synapse due to SMN having a function in axon RNA transport66, 67, 68 at the growth cones of motor neurons cultured from SMA mice. It has been proposed that hRNPQ/R66, 67 and ZBP69 participate with SMN in this complex and that the reduced β-actin transport leads to alteration of calcium channel distribution at the axon terminal139 which in turn could affect neurotransmitter release (see text). Lsm proteins 1 and 4 have been found in axons in an RNP complex.59 We suggest that it is possible that reduced SMN levels affect the assembly of Lsm proteins required for axonal transport of mRNA, leading to reduced expression of specific genes at the synapse. However, a functional biochemical assay linking reduced SMN levels to an alteration in the formation of the required complex for transport of mRNA is lacking (indicated by ?). Whether other Lsm proteins, such as Lsm14, associate with this complex in neurons is not known.
We have not indicated other potential or known SMN dependent assembly pathways, such as assembly of U7 snRNA, as it is not clear how alteration of this pathway would give rise to SMA. However, we cannot eliminate the possibility that other RNP assembly reactions are affected by reduced SMN levels. Lastly, it is possible to unite the two hypotheses where reduced snRNP assembly causes reduced splicing of a target gene that is critical for transport of mRNA to the motor neuron synapse.