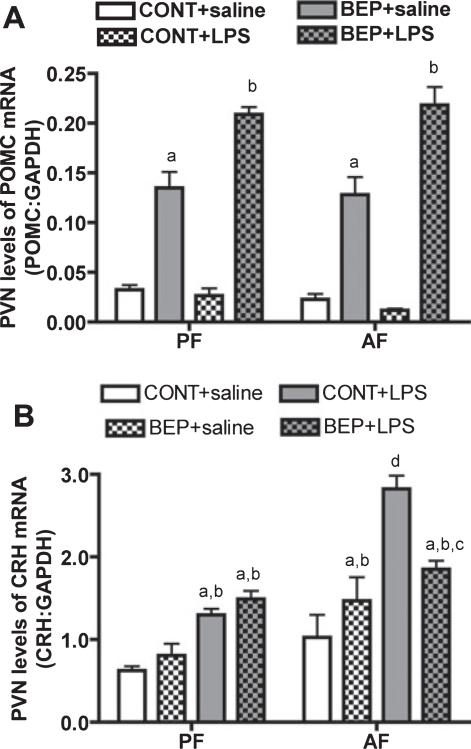
Fig. 2.
Physiological responses of transplanted cells in the PVN. Male rats (35- to 40-day old) fed during embryonic days 11 through 21 via dams; with alcohol (alcohol-fed rats; AF) or isocaloric liquid diet (pair-fed rats; PF) were transplanted with BEP cells (20,000 cells/1 μl) into the left PVN or nonviable BEP cells (CONT; 20,000 cells/1 μl) into the right PVN. After 2 weeks, rats underwent LPS or saline treatment and then 3 hours after they were sacrificed and the PVN tissues of these rats were collected and used for POMC or CRH measurements. POMC mRNA (A) and CRH mRNA (B) levels in the PVN lobe with BEP cells and in the contralateral lobe of the PVN with CONT after i.p. administration of LPS or of saline. n =6. POMC mRNA data identified no interaction between in utero feedings and cell treatments (F = 0.5116, df-3, p < 0.6781), while CRH mRNA data showed significant interaction between in utero feedings and cell treatments (F = 161.1, df-3, p < 0.001), ap < 0.001 versus PF + CONT + saline or AF + CONT + saline. bp <0.01 versus PF + CONT + LPS or AF + CONT + LPS. cp < 0.01 versus PF + BEP + saline. dp < 0.001 versus rest of the groups.