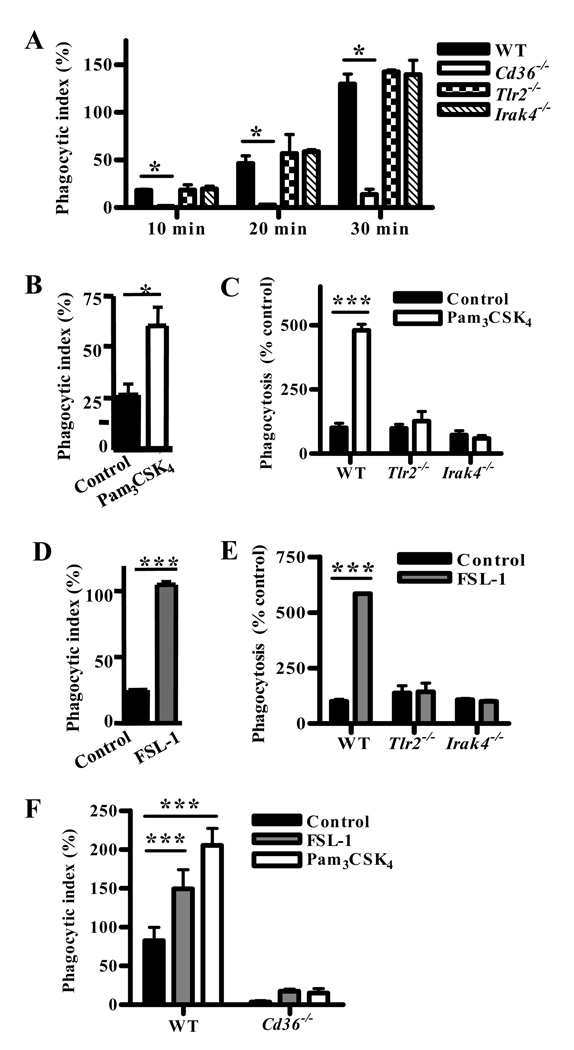
Fig. 4. Macrophage pre-stimulation by TLR2 agonists enhances CD36-mediated internalization in a TLR2-, IRAK4-, and CD36-dependent manner.
(A) Wild-type, Tlr2−/−, Irak4−/−, and Cd36−/− murine macrophages were incubated with α-CD36 EBABs over a 30 min time course, and phagocytic indices were determined. * indicates p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests. (B) Human and (C) murine macrophages were treated with medium alone or TLR2 agonist Pam3CSK4 (100 ng/mL) for 1 hr, followed by a 30 min α-CD36 EBAB internalization assay. (D) Human and (E) murine macrophages were treated with medium alone or CD36-dependent TLR2 agonist FSL-1 (20 ng/mL) for 1 hour prior to α-CD36 EBAB internalization. (F) Wild-type and Cd36−/− murine macrophages were pre-stimulated with medium alone, Pam3CSK4, or FSL-1 for 1 hr prior to α-CD36 EBAB internalization. * indicates p<0.05, ** p<0.01, and *** p<0.001 by Student’s t-test (human data) or two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-tests (murine data). Data shown are representative of three independent experiments.