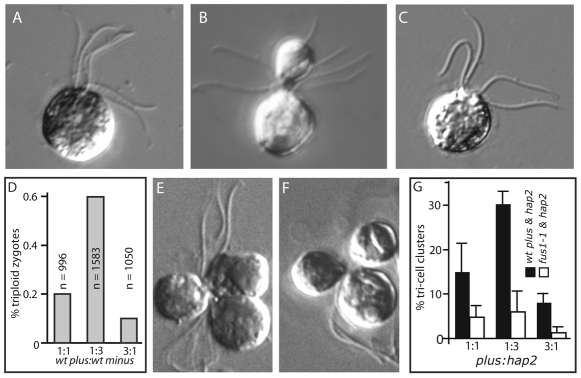
Fig. 1.
Triploid zygotes and tri-cell clusters. (A) Fully coalesced triploid zygote with six flagella emerging from the apical end of the cell. (B) Partially coalesced triploid zygote. (C) Typical diploid zygote with four flagella emerging from the apical end of the cell. (D) Triploid zygotes in mixtures of wild-type plus and minus gametes. Wild-type plus and minus gametes were mixed at the indicated ratios and the percent of zygotes that were triploid was determined by phase contrast microscopy. n=total number of zygotes counted. (E,F) Tri-cell clusters formed by adhesions between mating structures of wild-type plus and hap2 minus gametes mixed at a ratio of 1:3. (G) Wild-type plus or fus1-1 plus gametes were mixed with hap2 minus gametes at the indicated ratios and the percent of cells in tri-cell clusters was assessed.