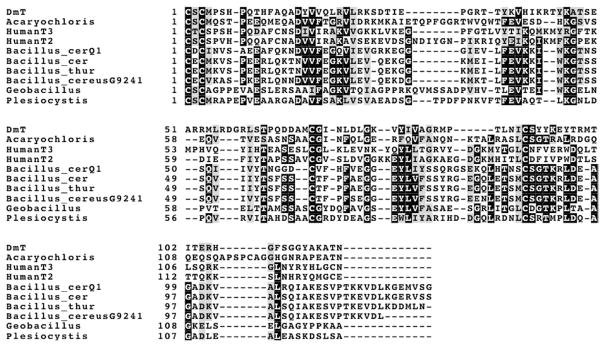
Fig. 4.
A comparison of some bacterial homologues with the N-domains of human TIMP-2 and -3 and Drosophila melanogaster TIMP. The sequences are from the following sources: Acaryochloris, hypothetic protein AM1_44443 from Acaryochloris marina MBIC11017; Bacillus_cerQ1, cbiN-domain protein from Bacillus cereus Q1; Bacillus_cer, hypothetical protein from Bacillus cereus G9241; Bacillus_thur, hypothetical protein BT9727_1673 from Bacillus thuringiensis serovar konkukian str. 97-27; Bacillus_cereus9241, hypothetical protein from Bacillus cereus G9241; Geobacillus, hypothetical protein GYMC10DRAFT_3737 from Geobacillus sp. Y412MC10; Plesiocystis, hypothetical protein PPSIR1 _33491 from Plesiocystis pacifica SIR-1. Other abbreviations are HumanT2, human N-TIMP-2; HumanT3, human N-TIMP-3; DmT, N-terminal domain of D. melanogaster TIMP.